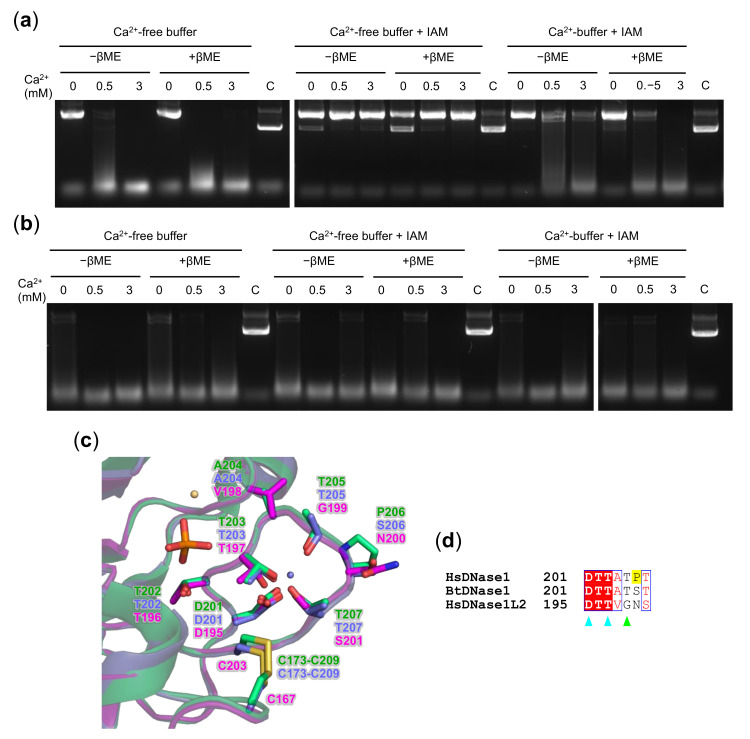
Figure 5.
Ca2+ protection of DNase1L2 reduced cysteines from alkylation. Agarose gel electrophoresis showing the effect of β–mercaptoethanol (βME) and iodoacetamide (IAM) on plasmid DNA digestion by (a) DNase1L2 and (b) rhDNase. The enzymes were in buffer supplemented with 1 mM CaCl2 or in CaCl2-free buffer. After treatment, reactions were assembled as described in Materials and Methods. (c) Superimposition of the DNase1L2 model (pink carbons) with the human DNase1 structure (4AWN; green carbons) and the bovine DNase1 structure (1ATN; violet carbons), showing the calcium-binding site I. Bound Ca2+ (violet), Mg2+ (light orange), and phosphate (orange) ions are shown. (d) Aligned sequences of human DNase1 (HsDNase1), bovine DNase1 (BtDNase1), and human DNase1L2 (HsDNase1L2). The position of the first amino acid of each sequence is on the right. The residue numbering is the same as in the structure in (c). Key residues are indicated as follows: Ca2+-binding site I, cyan triangles; DNA binding, green triangle; and the proline (P206) discussed in the text is highlighted in yellow.