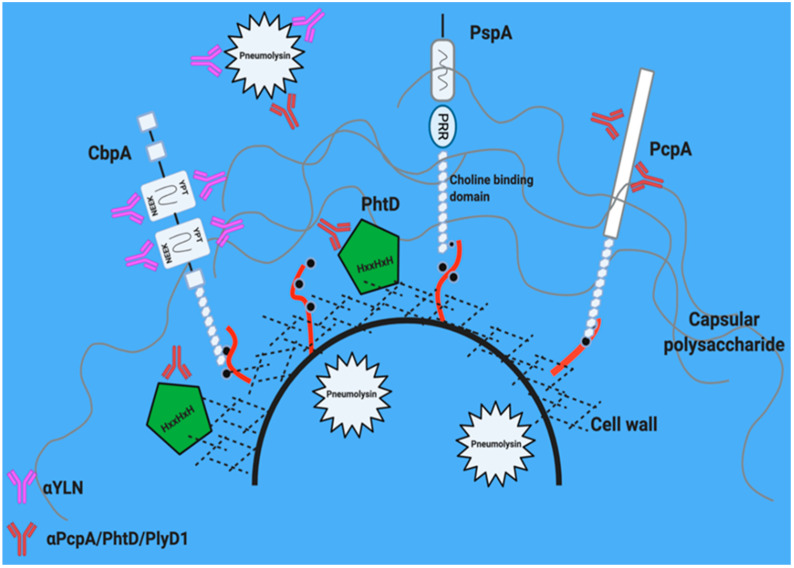
Figure 2.
Leading candidate proteins for multi-valent vaccines. There are several conserved bacterial proteins—both on the surface of the cell wall (hatched black lines with red teichoic acids) and present in the extracellular environment of the bacteria. Pneumolysin (white star) is a pore forming toxin that is localized within the cytoplasm, but is released during cell lysis. Pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA), choline binding protein (CbpA), pneumococcal choline binding protein (PcpA) and histidine triad protein D (PhtD) are surface proteins that have domains conserved across serotypes and contribute to pneumococcal pathogenesis. Antibodies (pink and red Y shapes) targeting each of these proteins have been shown to convey protection to animals against experimental disease. Thus, they have been formulated into vaccines for human clinical trials.