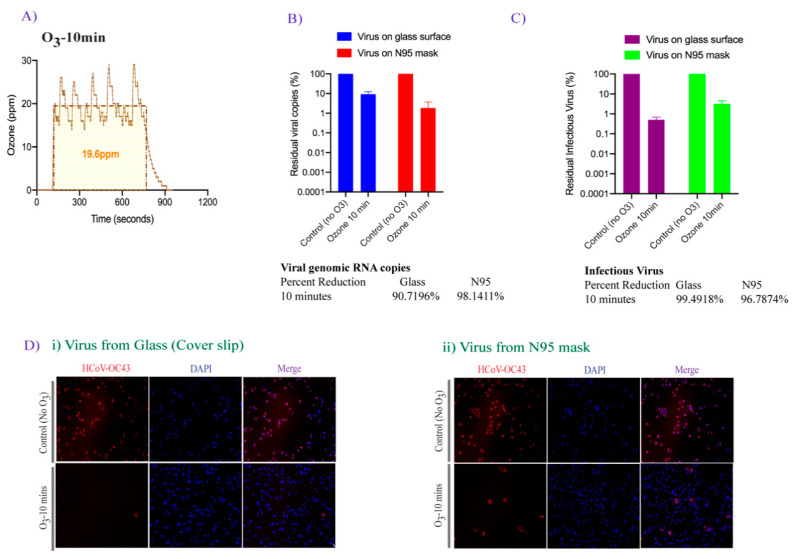
Figure 3.
The effect of 20 ppm-10 min ozone exposure on HCoV-OC43 viral genomic RNA stability and infectivity. (A). The plot depicting the average ozone dose (20 ppm-10 min) generated via FATHHOME device to which the virus was exposed. The ozone dose data were recorded using the connected FD-600-O3 ozone detector. (B). HCoV-OC43 virus (10 × 10 µL droplets) was applied on coverslips and N95 FFRs and exposed to 20 ppm ozone gas for 10 min. Total RNA was extracted and used for the detection of viral copies by qRT-PCR. (C). HCoV-OC43 virus (100 µL) was exposed to 20 ppm-10 min ozone treatment, collected, and used for the infection of A549-hACE-2 cells. Total RNA was extracted 48 h post-infection for the detection of intracellular viral genomic copies in a qRT-PCR assay. Viral copies were calculated based on a standard curve generated using the known amounts of virus (BEI Resources), and quantified with respect to untreated controls, set to 100%. (D). Untreated and ozone-treated HCoV-OC43 virus infected A549-hACE-2 cells were fixed and immune stained with HCoV-OC43 antibody (for nucleocapsid protein) for immunofluorescence assay. Virus internalization showed virus preferably localized on the membrane (red signals) in HCoV-OC43 infected cells. Nuclei were stained with TO PRO-3 (blue signals). The uninfected and infected cells were identified and quantified using automated Image J macro method.