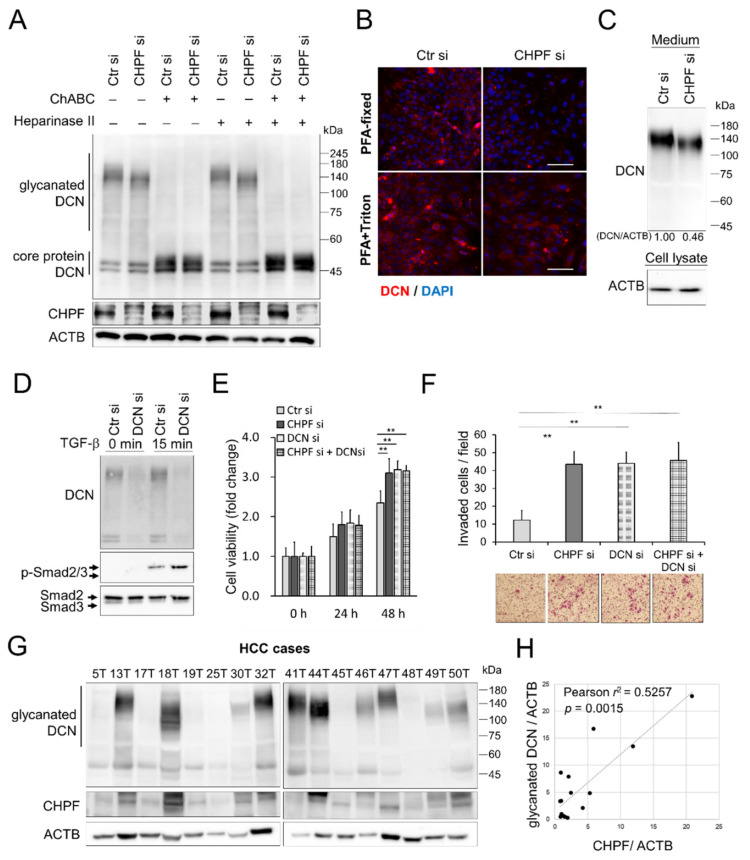
Figure 6.
Decorin is modified by CHPF and is involved in malignant phenotypes in HCC cells. (A) CHPF modified the CS chains on decorin (DCN). The molecular weight of glycanated decorin was decreased after CHPF knockdown in HA59T cells. Glycanated decorin was mostly shifted to the size of core protein after 2 h of digestion with chondroitinase ABC (ChABC). These results showed no difference with regard to heparinase II treatments. Blotting of ACTB was used as an internal control. (B) Immunostaining of DCN in controls and CHPF-silenced cells. Cells with paraformaldehyde (PFA) fixation are shown at the top. Images of PFA fixation, followed by triton X100 permeabilization, are shown at the bottom. The scale bar indicates 50 μm. (C) Secreted DCN in HA59T culture medium (1 × 106 of cells in 1 mL serum free medium for 24 h). Blotting of ACTB from attached cell lysate was used as a loading control. (D) Silence of DCN enhanced TGF-β signaling. Effects of DCN silencing on CHPF-mediated cell viability (E) and cell invasion (F). The HA59T cells were transfected with non-targeting control siRNAs (Ctr si), CHPF si, and/or DCN specific siRNAs (DCN si). Cells were subjected to CCK8 assay or transwell invasion assay. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01. The representative images are shown on the right. (G) Western blots of DCN and CHPF in 16 primary HCC tissues. ACTB was used as a loading control. (H) Correlations between CHPF protein expression and glycanated DCN in HCC tissues; Pearson r2 = 0.5257; p = 0.0015.