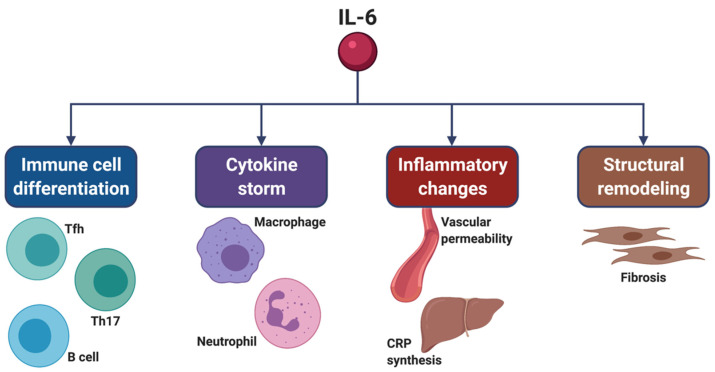
Figure 2.
Pleiotropic actions of IL-6, which targets many cell types and tissue districts. IL-6 promotes the differentiation of B cells, as well as of Th17 cells and Tfh cells. By contributing to the differentiation of Th17 cells, IL-6 also induces neutrophil recruitment and macrophage activation, which occur as relevant consequences of cytokine storm. Moreover, IL-6 increases vascular permeability and the hepatic synthesis of CRP, thus significantly contributing to the development and persistence of inflammation. IL-6 also induces tissue remodeling via stimulation of both fibroblast proliferation and production of extracellular matrix proteins. This original figure was created by the authors using BioRender.com. IL-6: interleukin-6; Th17: T helper 17 cell; Tfh: T follicular helper cells; CRP: C-reactive protein.