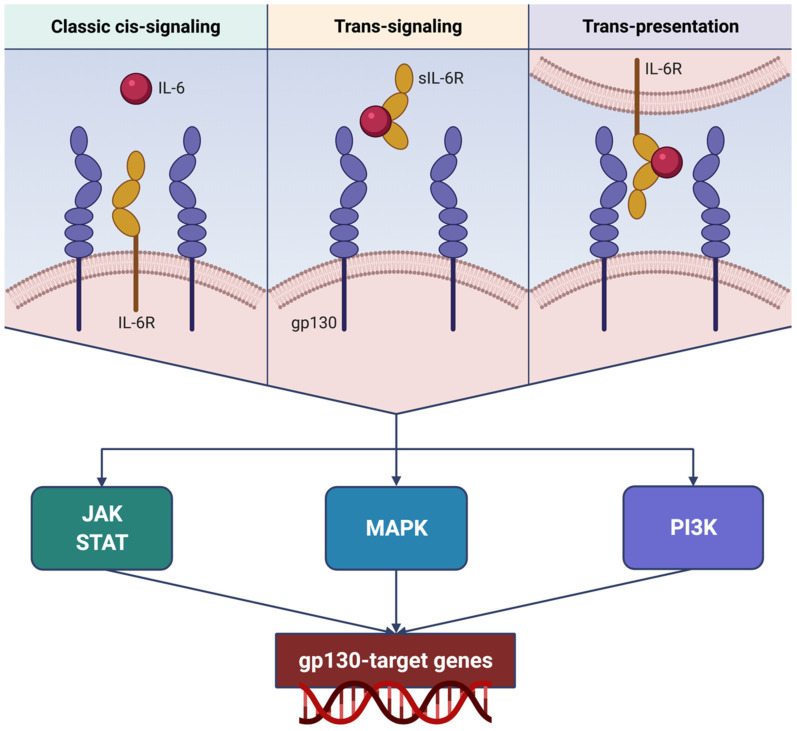
Figure 3.
Different mechanisms underlying IL-6R activation and signaling. IL-6 can either interact with membrane-bound IL-6R (classic cis-signaling), or bind to sIL-6R (trans-signaling), or even be trans-presented from dendritic cells through their surface IL-6R to T lymphocytes (trans-presentation). Classic cis-signaling, trans-signaling, and trans-presentation converge on downstream transduction pathways, consisting of dimeric gp130-dependent activation of complex networks including JAK/STAT, MAPK, and PI3K signaling modules. Via these intracellular enzyme systems, IL-6R-triggered biological signals reach the nucleus and stimulate gp130 target genes involved in cell growth and proliferation. This original figure was created by the authors using BioRender.com. IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-6R: interleukin-6 receptor; sIL-6R: soluble interleukin-6 receptor; gp130: glycoprotein 130; JAK: Janus kinases; STAT: signal transducers and activators of transcription; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinases; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase.