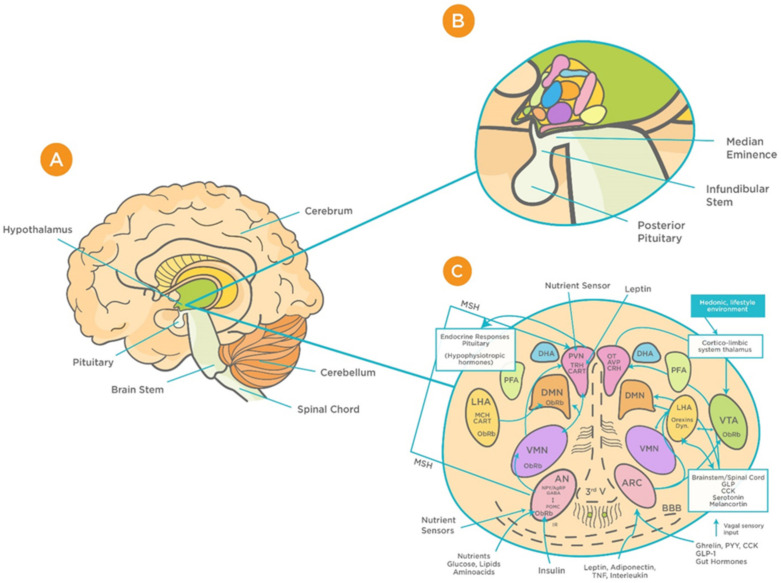
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the functional structure of hypothalamic circuits. (A) Location of hypothalamus within the ventral part of the diencephalon. (B) Location of hypothalamus in relation to the median eminence, infundibular stem, and pituitary glands. (C) Patterns of functional interaction between the hypothalamic nuclei (reproduced with permission from [48]). Abbreviations: AN: arcuate nucleus; AgRP: Agouti-related protein; AVP: arginine vasopressin; BBB: Blood brain barrier; CART: cocaine and amphetamine-regulated transcript; CRH: corticotrophin releasing hormone; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; VMN: ventromedial nucleus; OT: oxytocin; DMN: dorsomedial nucleus; PVN: periventricular nucleus; DHA: dorsal hypothalamic area; IR: insulin receptor; PFA: perifornical area; LHA: lateral hypothalamic area; MCH: Melanin-concentrating hormone; MSH: melanocyte-stimulating hormones; CN: suprachiasmatic nucleus; SON: supraoptic nucleus; POA: preoptic area; POMC: Pro-opiomelanocortin; PPY: Polypeptide; ObRb: Leptin receptor; MB: mammillary bodies; ME: median eminence; NPY: Neuropeptide; III-V: third ventricle; TRH, thyrotropin-releasing hormone.