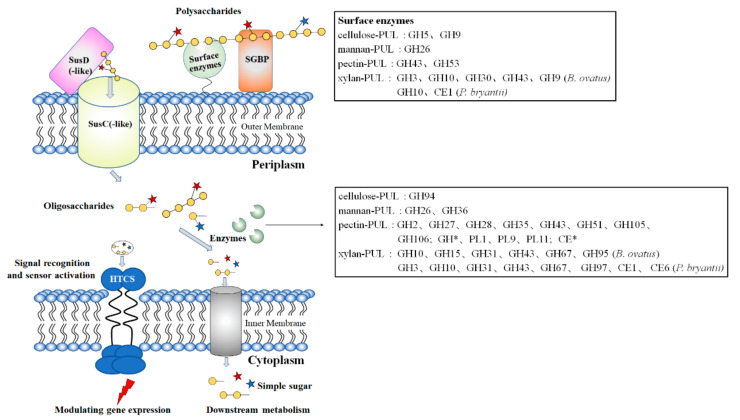
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the Bacteroides polysaccharide utilization systems (PULs). Polysaccharide molecule is bound to a SGBP on the Bacteroides cell membrane surface and degraded into large fragments by the action of surface enzymes. Then the oligosaccharides, which are transported across the outer membrane and into the periplasmic space via the TonB-dependent transporter SusC/SusD-like for further processing. The oligosaccharides are subsequently hydrolyzed into simple sugar by the enzymes located in the cytoplasm space. The inner-membrane associated symporter protein transports the products into the cytosol for metabolism. The HTCS-like regulator is required to induce expression of the polysaccharide utilization genes through a series of signal cascade reactions. GH, glycoside hydrolase; PL, polysaccharide lyase; CE, carbohydrate esterase; *, new family. Yellow circles stand for the monosaccharides that form the backbone of a polysaccharide. The red and blue stars represent different groups on the side chain of the polysaccharides.