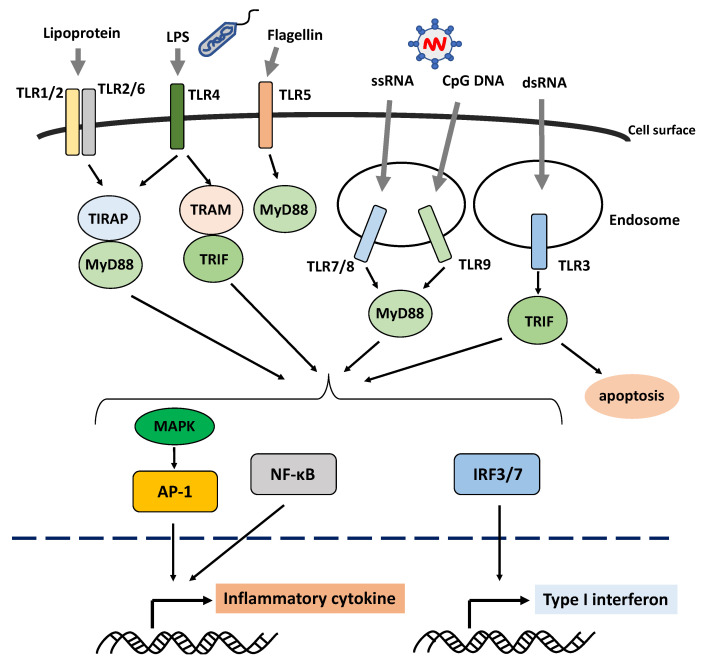
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the activation of the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are the pattern-recognition receptors, which recognize different pathogen- or danger-associated molecular patterns. TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, and TLR6, which are involved in the recognition of proteins and fats, are mainly localized on the cell surface, whereas TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9, which are involved in the recognition of nucleic acids, are mainly localized within the cells in the endosomes and endoplasmic reticulum. The TLR recognition of their ligands leads to the production of inflammatory cytokines and type I interferon via downstream molecules. Abbreviations: AP-1: activator protein 1; IRF: interferon regulatory factor; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; TIRAP: toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adapter protein; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TRAM: TRIF-related adaptor molecule; TRIF: TIRAP inducing interferon β.