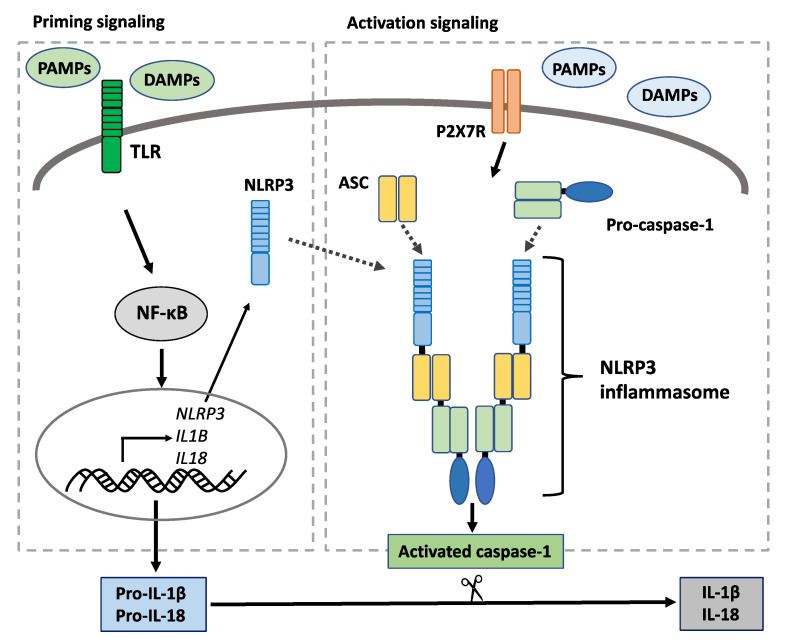
Figure 3.
Mechanism of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. NLRP3 inflammasomes are formed by priming and activation signaling. In the priming signaling, several pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) bind to the pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) such as Toll-like receptors and activate the NF-κB signaling pathway, which leads to the upregulation of NLRP3, pro-interleukin (IL)-1β, and pro-IL-18. In the activation signaling, various PAMPs, DAMPs, or intracellular changes induce the formation of the NLRP3 inflammasome composed of NLRP3 as a PRR, pro-caspase-1, and adapter proteins such as the apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain that connects NLRP3 and pro-caspase-1. Then, the inflammasome complex activates pro-caspase-1. The activated caspase-1 cleaves the pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into IL-1β and IL-18, which are biologically active forms. Abbreviations: ASC: apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; DAMP: danger-associated molecular pattern; IL: interleukin; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; NLRP3: NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; TLR: Toll-like receptor.