Fig 1.
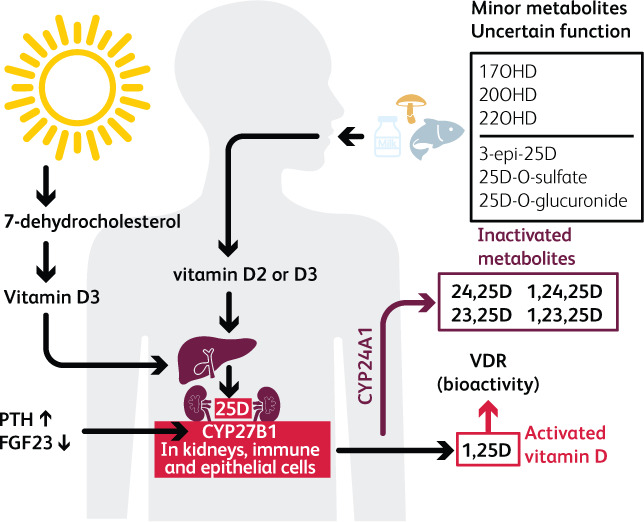
The complexity of vitamin D metabolism. D2 is from plant sources via ultraviolet action on ergosterol and D3 from animal sources via ultraviolet action on 7-dehydrocholesterol. Activation is via 25-hydroxylation in the liver followed by 1α-hydroxylation (CYP27B1) in kidneys, immune cells and many epithelia, to 1,25(OH)2D. Increased FGF23 suppresses 1α-hydroxylation. Free 25(OH)D appears to be preferentially taken up by monocytes,19 so the reduction in DBP in illness may have a protective effect via increased availability of free 25(OH)D. Either 25(OH)D or 1,25(OH)2D can be degraded via 24-hydroxylation (CYP24A1) to 24,25(OH)D or 1,24,25(OH)3D respectively.
