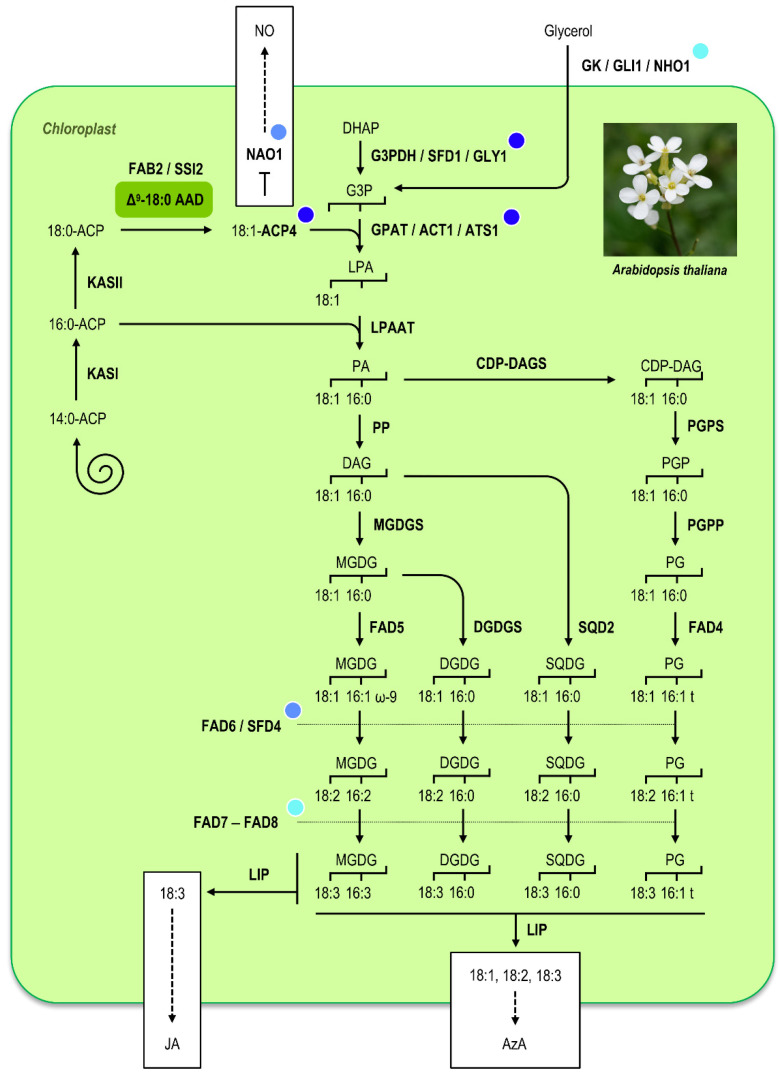
Figure 3.
Lipid metabolism in the chloroplasts of Arabidopsis thaliana. The scheme depicts the different pathways involved in the biosynthesis of fatty acids and the elaboration of membrane lipids in the chloroplasts of A. thaliana. For the sake of clarity, export of fatty acids from the plastids and the eukaryotic lipid metabolic pathway have been omitted. Production of oleic acid by the Δ9-stearoyl–ACP desaturase FAB2/SSI2 is highlighted in green. Blue-colored circles denote enzymatic steps whose blockage (by mutation of corresponding genes) complements the fab2/ssi2 mutant phenotype: darker shades of blue denote full phenotypic reversion while lighter shades of blue denote partial phenotypic reversion. Lipid-derived signaling molecules (JA and AzA) and NO, whose biosynthesis is regulated by oleic acid, are presented on a white background. AAD, acyl–acyl carrier protein desaturase; ACP, acyl carrier protein; AzA, azelaic acid; CDP-DAG, cytidinediphosphate-diacylglycerol; DAG, diacylglycerol; CDP-DAGS, cytidinediphosphate-diacylglycerol synthase; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; DGDG, digalactosyldiacylglycerol; DGDGS, digalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase; FAD, fatty acid desaturase; G3P, glycerol-3-phosphate; G3PDH, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GK, glycerol kinase; GPAT, glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; JA, jasmonic acid; KAS, fatty acid synthase complex comprising 3-ketoacyl-ACP synthase; LIP, lipase; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPAAT, 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; MGDG, monogalactosyldiacylglycerol; MGDGS, monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase; NAO1, NITRIC OXID ASSOCIATED1; NO, nitric oxide; PA, phosphatidic acid; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PGP, phosphatidylglycerol-phosphate; PGPP, phosphatidylglycerol-phosphate phosphatase; PGPS, phosphatidylglycerol-phosphate synthase; PP, phosphatidate phosphatase; SQD2, UDP-sulfoquinovose:diacylglycerol sulfoquinovosyltransferase; SQDG, sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol. Picture credit: [81].