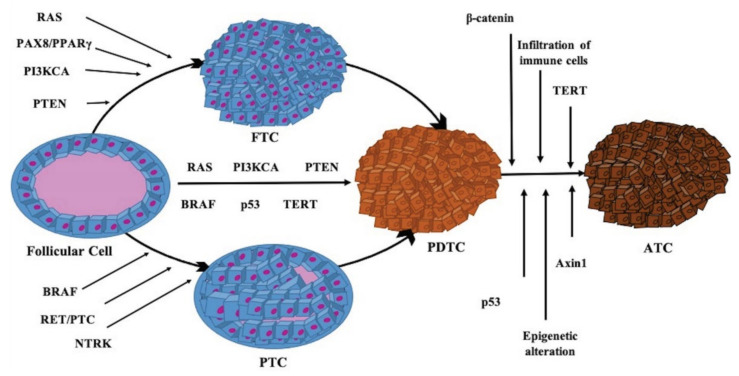
Figure 2.
Molecular alterations that lead to mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K), and receptor kinase pathways activation and promote the progression of follicular thyroid cells to papillary (PTC) and to follicular thyroid cancer (FTC). Additional mutations and rearrangements and an increase of MAPK and PI3K pathways signaling promote further progression to poorly differentiated thyroid cancer (PDTC). Further genetic events, especially involving p53, epigenetic alteration, and infiltration of immune cells, promote the onset of anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC).