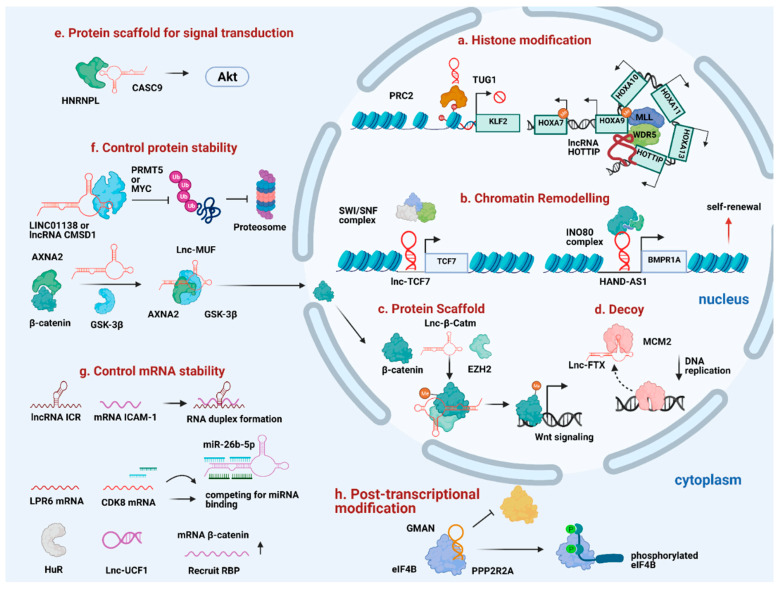
Figure 2.
Diverse mechanism of lncRNAs in promoting HCC progression. (a) TUG1 and HOTTIP act as guide to recruit histone modifiers to the specific loci. (b) Lnc-TCF7 and HAND-AS1 recruit SWI/SNF complex to specific gene promoters to promote self-renewal. (c) Lnc-β-Catm reinforces protein-protein interaction and controls protein stability. (d) Lnc-FTX serves as a molecular decoy to move MCM2 away from the chromatin. (e) Cytoplasmic lncRNAs like CASC9 interacts with HNRNPL to promote HCC progression. (f) LINC01138, CMSD1, and Lnc-MUF interact with protein partners to control protein stability. (g) Some lncRNAs control mRNA stability through forming RNA duplex with target mRNA, acting as competitive sponge for miRNA binding or recruit RNA-binding protein to stabilize target mRNA stability. (h) GMAN regulates post-transcriptional modification by disrupting the interaction between target protein and protein-modifying enzyme.