Figure 1.
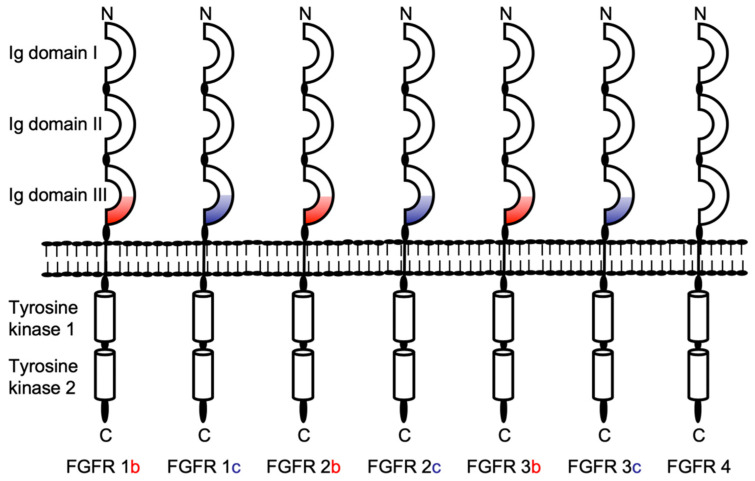
Schematic overview of the structure of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family of receptor tyrosine kinases. FGFRs are highly conserved transmembrane proteins containing an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic kinase domain with two adjacent tyrosine residues. The extracellular ligand-binding domain contains three immunoglobulin (IG)-like domains, Ig I, Ig II, and Ig III, which are important for receptor dimerization. Alternative splicing of the second half of the third Ig-like domain gives rise to alternative IIIb (red) or IIIc (blue) isoforms of FGFRs 1 to 3. The proteins coded by FGFRs 1 and 2 can also alternatively produce additional splice variants, generating truncated isoforms [5].