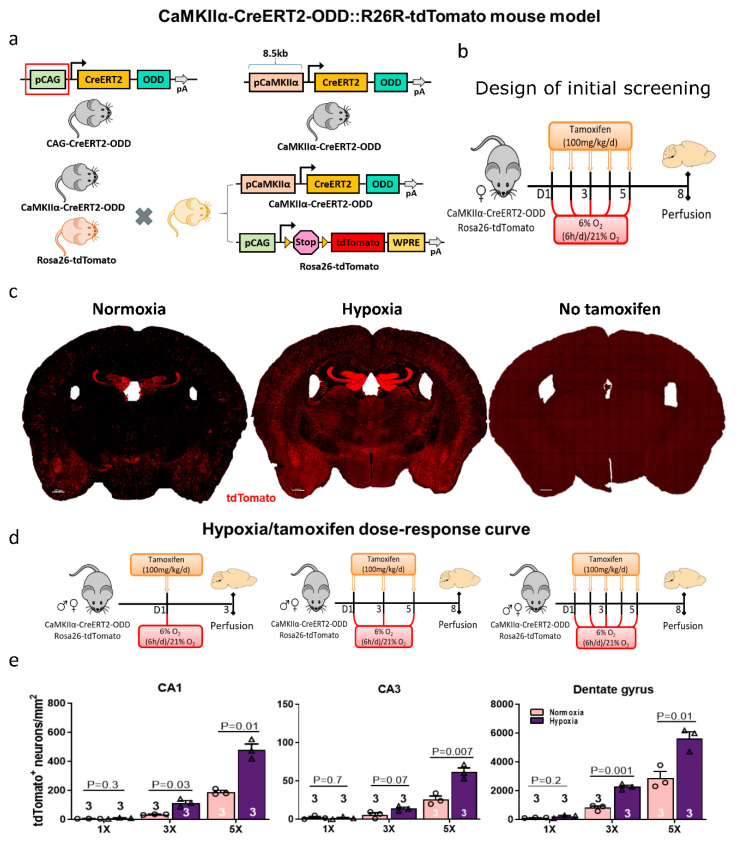
Figure 1.
Generation and first characterization of excitatory neuron-specific CaMKIIα-CreERT2-ODD::R26R-tdTomato hypoxia reporter mice. (a) Schematic representation of the CAG-CreERT2-ODD construct where the CAG promoter was excised using SpeI and EcoRI restriction enzymes to obtain the vector backbone (CreERT2-ODD-pA). Subsequently, the excitatory neuronal promotor CaMKIIα of 8.5 kb was inserted into CreERT2-ODD-pA to generate the CaMKIIα-CreERT2-ODD-pA vector. Next, the linearized vector was used for the generation of CaMKIIα-CreERT2-ODD expressing transgenic mice. These were crossed with CAG-Rosa26-tdTomato reporter mice. Permanent labelling of hypoxic neurons is achieved via Hif-1α oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODD) stabilization upon tamoxifen injection. (b) Experimental design: For an initial screening, CaMKIIα-CreERT2-ODD::R26R-tdTomato hypoxia reporter mice received tamoxifen five times over five days, each time followed by exogenous hypoxia (6% O2 for 6 h) versus normoxia (21% O2), and mice were sacrificed on day eight. (c) Representative coronal images of five-times tamoxifen-injected CaMKIIα-CreERT2-ODD::R26R-tdTomato mice under normoxic or hypoxic conditions. The corn oil control (‘no tamoxifen’) shows only very few tdTomato+ (red) neurons, i.e., minimal tamoxifen-independent Cre-activity. Scale bar represents 500 µm. (d) Experimental scheme of the hypoxia/tamoxifen dose response curve in CaMKIIα-CreERT2-ODD::R26R-tdTomato mice. (e) Quantification of tdTomato+Ctip2+ double-positive neurons in CA1, CA3 and dentate gyrus from eight-week-old mice of equally distributed mixed gender. Unpaired Student’s t-test (two-tailed, Welch’s corrections) was used for statistical analysis between groups; n numbers given in graphs; error bars indicate standard error of mean (SEM).