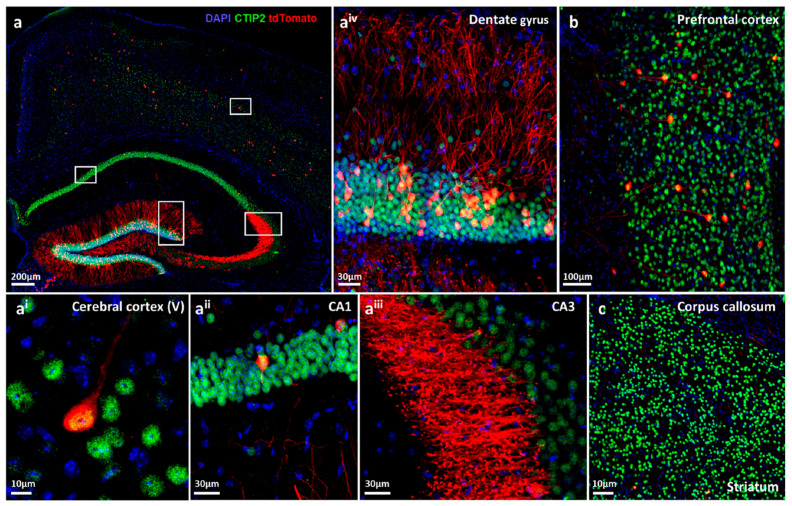
Figure 2.
Immunohistochemical characterization of functional hypoxic pyramidal neurons in CaMKIIα-CreERT2-ODD::R26R-tdTomato reporter mice. (a) Overview image of an eight-week-old female mouse after exposure to complex running wheel (CRW) showing distinct labelling of neurons with tdTomato fluorescent protein (red), co-immunostained with the neuronal marker Ctip2 (green) and DAPI (blue) as nuclear counterstain. White frames denote magnifications given in ai–aiv. (ai) Image of cortical layer V showing a neuron with tdTomato+ and Ctip2+ co-localized signal. (aii) Some cornu ammonis (CA1) pyramidal neurons are tdTomato positive. (aiii) In CA3, just a few neuronal cell bodies display the tdTomato signal; however, strong staining is observed in stratum lucidum, rendering neuronal morphological details such as dendritic spines and synapses easily distinguishable at high resolution. (aiv) Close-up image of the superior plate of the dentate gyrus, demonstrating densely tdTomato-expressing granular neurons and remarkable labelling of neutropil. (b) A subset of neurons in prefrontal cortex and their processes are also tdTomato labelled. (c) CaMKIIα expressing tdTomato+ neurons are sparsely present in the striatum. Scale bars represent 200 µm (a), 10 µm (ai, c), 30 µm (aii, aiii and aiv), and 100 µm (b).