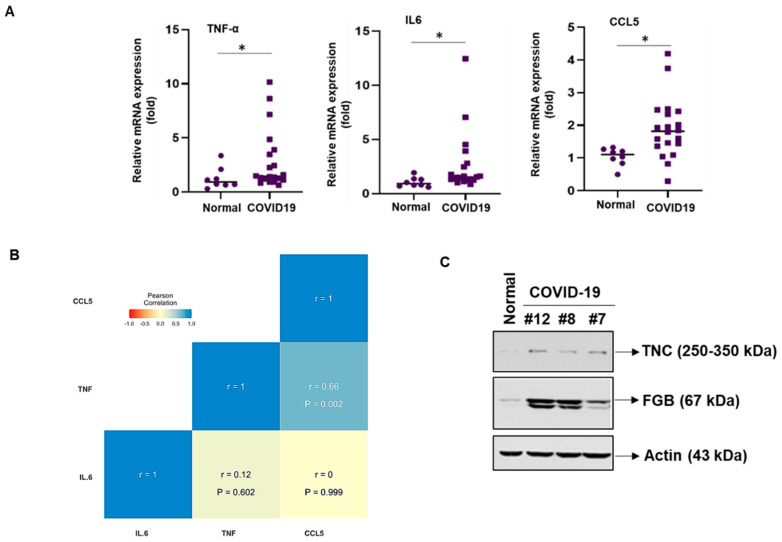
Figure 4.
Exposure of hepatocytes to exosomes from COVID-19 plasma triggers pro-inflammatory molecules. (A) Immortalized human hepatocytes (IHHs) were exposed to normal and COVID-19 exosomes for 48 h and total RNA was isolated. Relative mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and C–C motif chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5) in cells treated with COVID-19 exosomes (n = 20) or normal exosomes (n = 8) were examined by qRT-PCR and represented by dot plots. We used 18s rRNA as an internal control. Small bar indicates standard error (* p < 0.05). (B) Pearson correlation analysis among expressions of the TNF-α, IL-6, and CCL5 in the hepatocytes exposed with patient exosomes. (c) Huh7 cells were exposed with normal and COVID-19 exosomes for 48 h and cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis for TNC or FGB using specific antibodies. The membrane was reprobed for actin as an internal control.