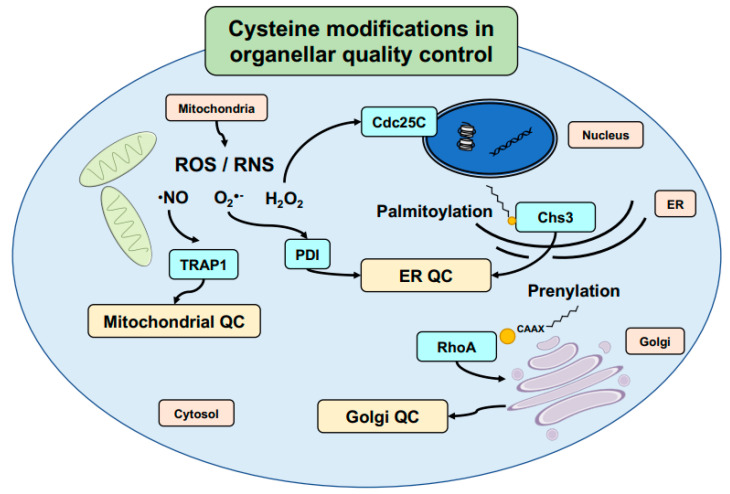
Figure 3.
Thiol-modifications define protein folding and translocation. Thiol modifications come in many forms, ranging from reactive oxygen/nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) to lipid modifications during protein maturation. Various individual proteins have been found to have redox-regulated functional changes affecting organellar quality control. Cysteine modifications on chaperones such as TRAP1 and PDI regulate quality control in the mitochondria and ER, respectively, while lipid modifications play additional roles in protein translocation within the cell. Palmitoylation of Chs3 regulates its proper exit from the ER and prevents its aggregation, while prenylation of RhoA alters its interactions with the SmgGDS chaperone. These and other cysteine modifications regulate various additional processes within the cell, such as the cell cycle in the case of hydrogen peroxide regulation of the checkpoint control protein Cdc25C.