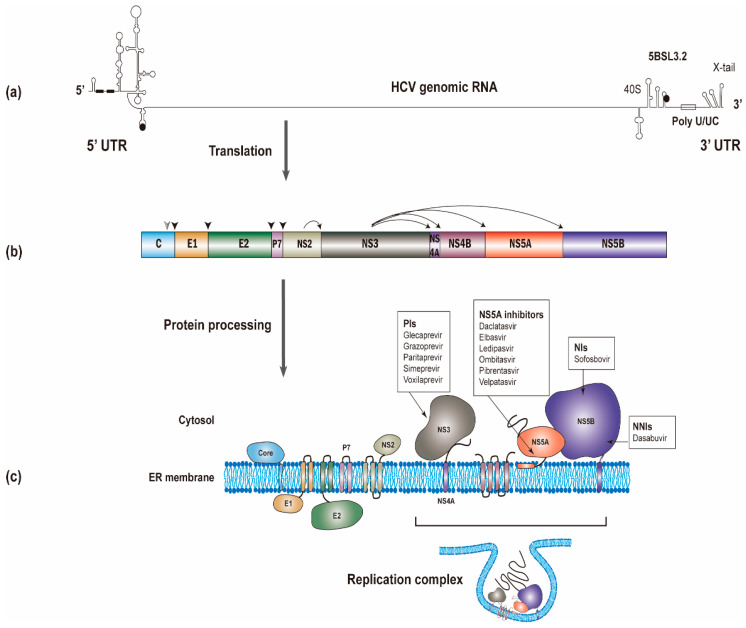
Figure 1.
The synthesis of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) proteins. (a) The start and stop codons for protein translation were marked by black circles, while two recognition sites on the 5’ UTR for miR-122 were marked by black rectangles. (b) The polyprotein is co- and post-translationally cleaved by cellular or viral proteases to yield the structural proteins (core, E1 and E2) and the nonstructural proteins (p7, NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A and NS5B proteins). The core, E1, and E2 are processed by cellular signal peptidase (filled arrowhead). A mature core protein will be generated after further cleavage by signal peptide peptidase (empty arrowhead). The NS2/NS3 junction site is cleaved by the NS2-NS3 auto-protease, and the remaining nonstructural proteins are processed by the NS3/4A proteinase. (c) All of the HCV proteins are directly or indirectly associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. Currently used anti-HCV direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) target NS3, NS5A, and NS5B, respectively. NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B proteins will form the replication complex.