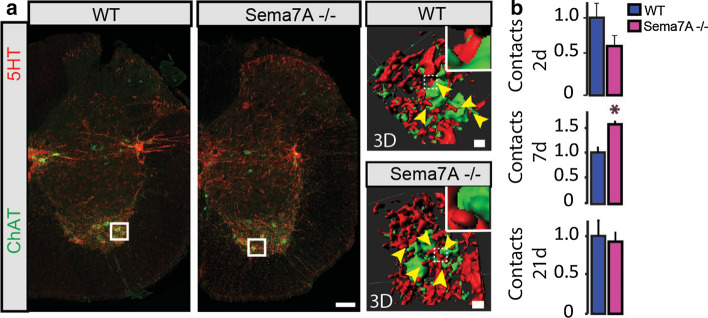
Fig. 4.
Deletion of Sema7A triggers only transient changes in the contact formation rate onto motoneurons following spinal cord injury. a Confocal images of putative contacts between serotonergic terminals and motoneurons in the lumbar cord of Sema7A deficient and WT mice and 3D reconstruction of the contacts using Imaris software (yellow arrowheads indicate putative sites of contacts and insets represent areas of contact). b Quantification of the number of contacts between serotonergic terminals (red) and motoneurons labeled with Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT; green) (n = 3 per group, except at 2 days nWT = 4; p values: 2 days = 0.5318; 7 days = 0.0134; 21 days = 0.7723; all Welch’s T test). Scale bars equals 100 µm and 20 µm in the Imaris reconstruction in (a)