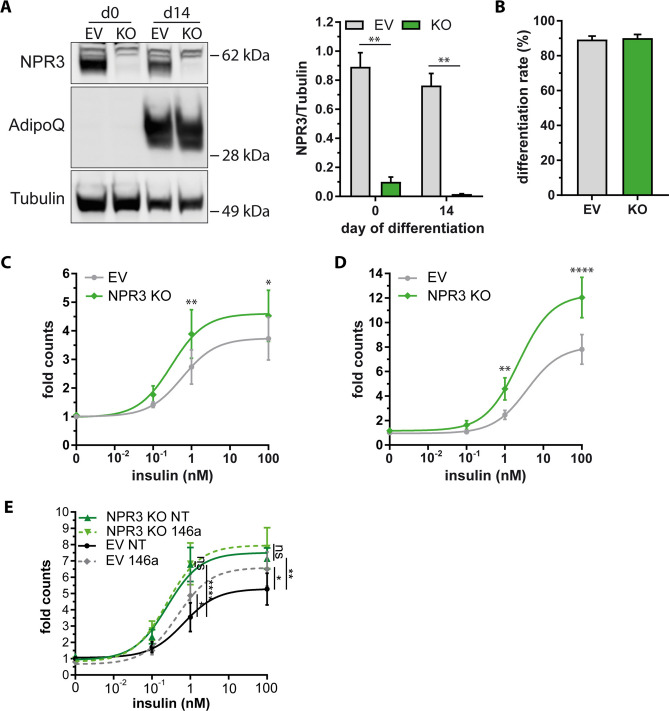
Fig. 8.
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated NPR3 ablation increases insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and de novo lipogenesis. a Representative Western blot for NPR3 (60 kD) and adiponectin (AdipoQ) in SGBS pre-adipocytes (d0) and adipocytes (d14) in control cells (EV) and NPR3 KO cells with densitometric analysis displayed as mean and SEM of 4 independent experiments in relation to tubulin. b Differentiation rates of adipocyte cultures (adipocytes/total cells). c Insulin-dependent glucose uptake was measured by scintillation counting and normalized to the basal rate of control cells (0 nM insulin). d Insulin-dependent de novo lipogenesis was measured by scintillation counting and normalized to the basal rate of control cells (0 nM insulin). e Insulin-dependent glucose uptake in control (EV) and NPR3 KO cells transfected with non-targeting (NT) or miR-146a mimic was measured by scintillation counting and normalized to the basal rate of EV cells (0 nM insulin). Data are displayed as mean and SEM of 5 (c) and 4 (d) independent experiments. Statistics: (a) two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (c and d) two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction and non-linear fit with three parameters. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001