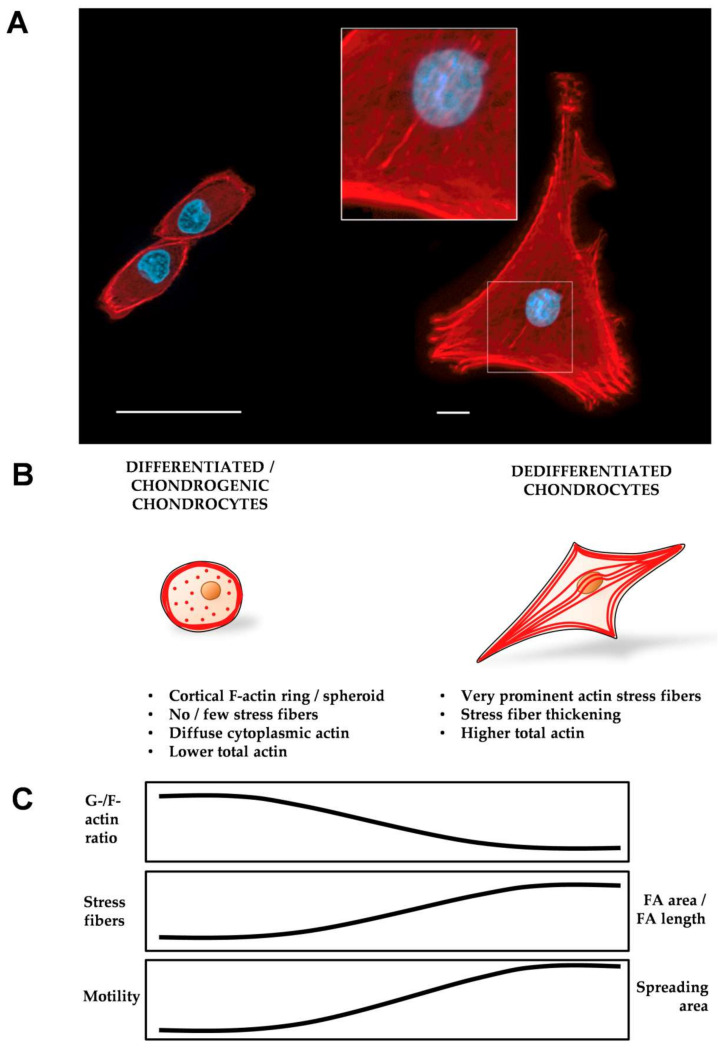
Figure 3.
(A) Representative 40x images of primary hCHs with different morphologies and the F-actin distribution on day 1 of cultivation, acquired with an AxioObserver-Z1, Zeiss, Germany. Left side: CHs cultured on a glass substrate coated with fibronectin. The image was taken with oil immersion. Right side: a CH cultured on a tissue culture polystyrene substrate. Red: F-actin, blue: nucleus. Scale bar: 50 µm. (B) Schematic actin organization, FA area, spreading area, and motility related to the CH differentiation status. Differentiated and round CHs have a cortical F-actin spheroid that appears as a “ring” in 2D and punctate (freckled) actin in the cytoplasm [70,71,72,169,170,175,196], and have low total actin. (C) A high G-/F-actin ratio [71], little or no SFs [70,71,72,196], a small FA area, small spreading area, and low motility [170] characterize differentiated CHs. Dedifferentiated, fibroblastic CHs have prominent, thick SFs [70,71,72,170,175,196], a high total actin, a low G-/F-actin ratio [71], a large focal adhesion (FA) area, large spreading area, and high motility [170].