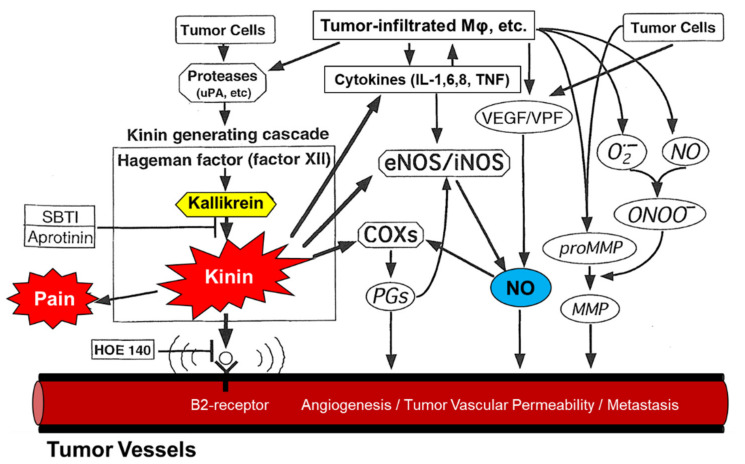
Figure 1.
The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature. The mechanism of this tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting depends on various effectors affecting vascular tone, as shown here. Aprotinin is an inhibitor of kallikrein; HOE-140 is a peptide antagonist of kinin. SBTI, soybean trypsin inhibitor; NO, nitric oxide; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; iNOS, inducible form of nitric oxide synthase; COXs, cyclooxygenases; PGs, prostaglandins; MMP, metalloproteinase; ONOO−, peroxynitrite; O2−, superoxide anion radical; MΦ, macrophage; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VPF, vascular permeability factor; uPA, urokinase plasminogen activator; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; B2 receptor, bradykinin B2 receptor (see also Supplementary Figure S1, adapted from ref [23]).