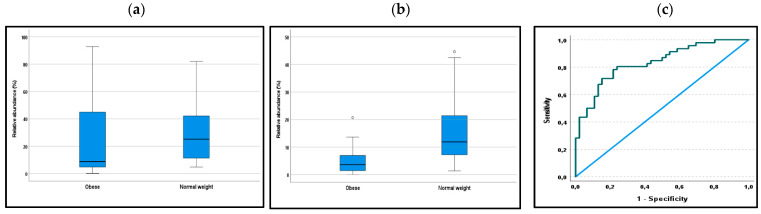
Figure 1.
(a): The relative abundance (%) of 17 bacteria with significant differences between subjects with morbid obesity and normal weight. (b) shows the corresponding results of a post hoc analysis of 8 bacteria that showed the best separation between the groups. The figures show the interquartile ranges, and the circles show two outliers. The differences between the groups were statistically significant (p = 0.001 and p < 0.001, respectively; Mann–Whitney U-test). (c): The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve shows the eight selected bacteria’s diagnostic properties for the diagnosis of obesity. The AUC is 0.83 (95% CI: 0.75–0.92; p < 0.001).