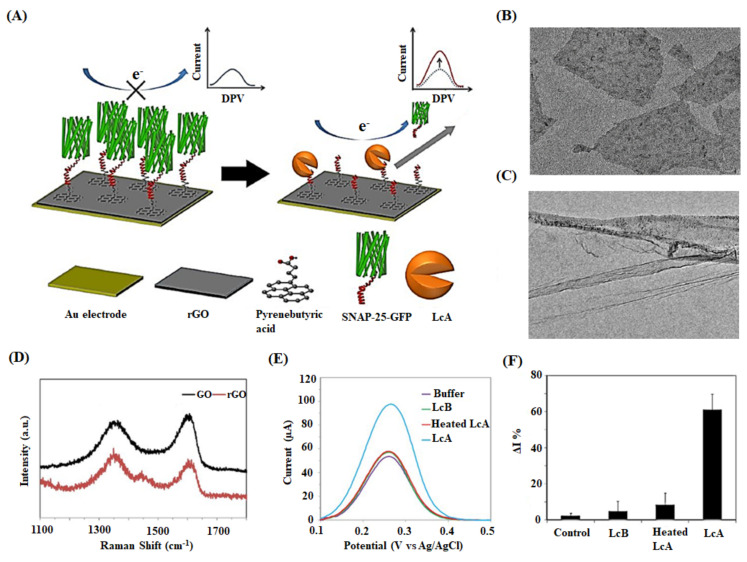
Figure 6.
(A) Schematic diagram illustrating the detection mechanism of an rGO-based biosensor. SNAP-25-GFP peptide is immobilized on the rGO surface, which is previously conjugated with pyrenebutyric acid. The target BoNT-LcAs specifically cleave SNAP-25-GFP molecules, detaching them from rGO/Au electrode surface. The detection of enzymatic activity decreases the hindrance of redox probes transfer on electrodes resulting in increased electrochemical currents. (B) TEM image of rGO flakes and (C) rGO sheets with ripples and wrinkles. (D) Raman spectra of GO and rGO. (E) Specificity testing of control buffer and fresh BoNT-LcA, heated BoNT-LcA, and fresh BoNT-LcA at the concentration of 1 ng mL−1. (F) Relative DPV peak current change (ΔI%) for the same samples [143].