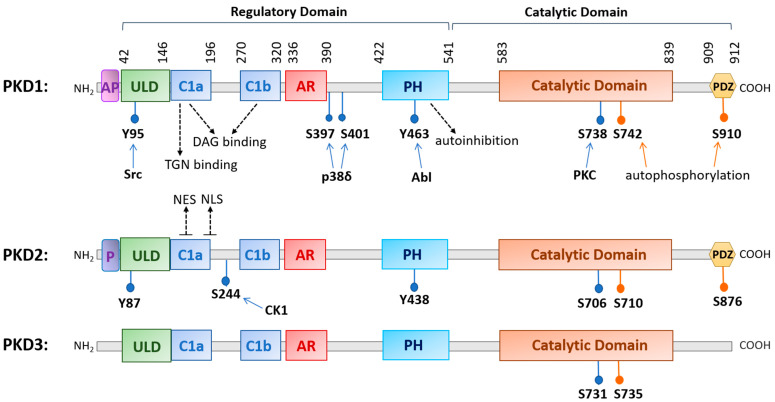
Figure 1.
A diagram illustrating the conserved structural domains and major phosphorylation sites in human protein kinase D (PKD) isoforms. The structure of PKD contains a newly identified ubiquitin-like domain (ULD) for dimerization, a C1 domain (Cla and Clb) that binds diacylglycerol, a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain for autoinhibition, a catalytic domain for substrate phosphorylation, and a PDZ domain in PKD1 and PKD2 for protein interactions. Other domains with less known functions are the acidic amino-acid-rich region (AR) and an alanine–proline-rich region (AP) for PKD1 and a proline-rich region (P) for PKD2. Major phosphorylation sites and the upstream kinases that confer the phosphorylation are indicated as well as the nuclear export signal (NES) and nuclear localization signal (NLS) for PKD2. Abbreviations: trans-Golgi network (TGN), Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 (Abl), casein kinase 1 (CK1).