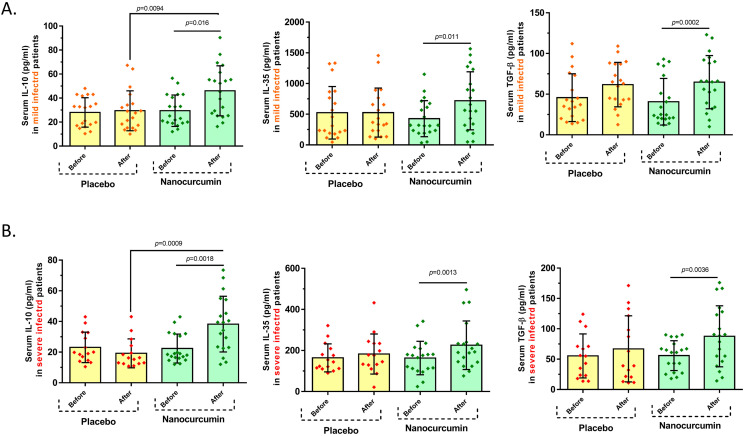
Fig. 4.
The serum secretion levels of Treg cell cytokines in Nanocurcumin and placebo-treated groups in mild and severe COVID-19 patients. A. In mild COVID-19 patients, treatment notably increased the serum concentration of IL-10 (P = 0.016), IL-35 (P = 0.011), and TGF-β (P = 0.0002) cytokines in comparison with pre-treatment condition in the Nanocurcumin-treated group; however, no significant changes in serum secretion levels of IL-10, IL-35, and TGF-β were found in the placebo group after treatment vs. before treatment. Also, the serum secretion level of IL-10 was considerably higher in the Nanocurcumin-treated group than in the placebo group after treatment (P = 0.0094), but no significant differences were observed in secretion levels of IL-35 and TGF-β among Nanocurcumin and placebo-treated groups, after treatment. B. In severe patients, the secretion levels of IL-10 (P = 0.0018), IL-35 (P = 0.0013), and TGF-β (P = 0.0036) cytokines were meaningfully higher in post-treatment with Nanocurcumin in the treated group when compared with pre-treatment condition. Besides, the serum secretion level of IL-10 was found to be considerably increased in the Nanocurcumin-treated group in comparison with the placebo-treated group after treatment (P = 0.0009). No significant alterations in the serum secretion levels of cytokines were observed in the placebo-treated group after treatment vs. before treatment. Mild patient group, n = 40; severe patient group, n = 40; Nanocurcumin treated group, n = 20; placebo-treated group, n = 20. Results are given as, mean ± SD. (+) in graphs indicates the mean. P < 0.05 describes statistically significant. COVID-19, Coronavirus disease 2019; Treg, T-regulatory cell; IL, interleukin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta.