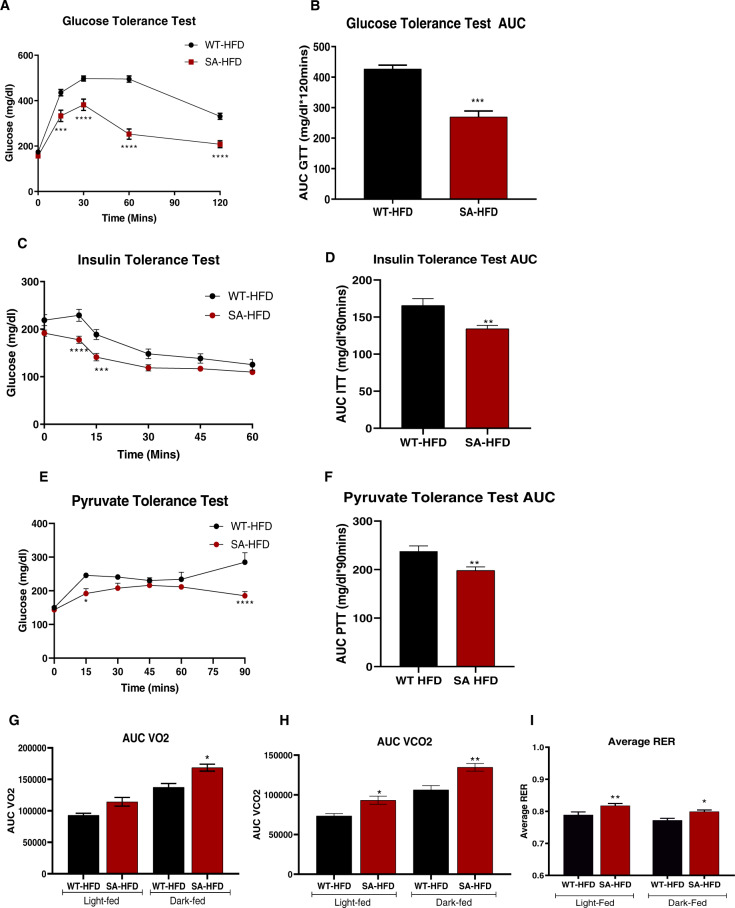
Fig. 4. SA knock-in mouse model has improved metabolic capacity under conditions of diet-induced obesity.
A Glucose tolerance test excursion curve and B glucose tolerance test area under curve after 6 weeks of HFD. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5/group; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs WT-HFD). C Insulin tolerance test excursion curve and D insulin tolerance test area under curve after 6 weeks of HFD. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5/group; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs WT-HFD). E Pyruvate tolerance test excursion curve and F pyruvate tolerance test area under curve after 6 weeks of HFD. Data are presented as means ± SEM (WT-HFD n = 5, SA-HFD n = 9; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 vs WT-HFD). G Volume of O2 consumption H volume of CO2 production, and I respiratory exchange ratio of mice was measured and calculated using CLAMS monitoring system as described previously after 12 weeks of HFD [27]. Data are presented as means ± SEM (WT-HFD n = 5, SA-HFD n = 4; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs WT-HFD).