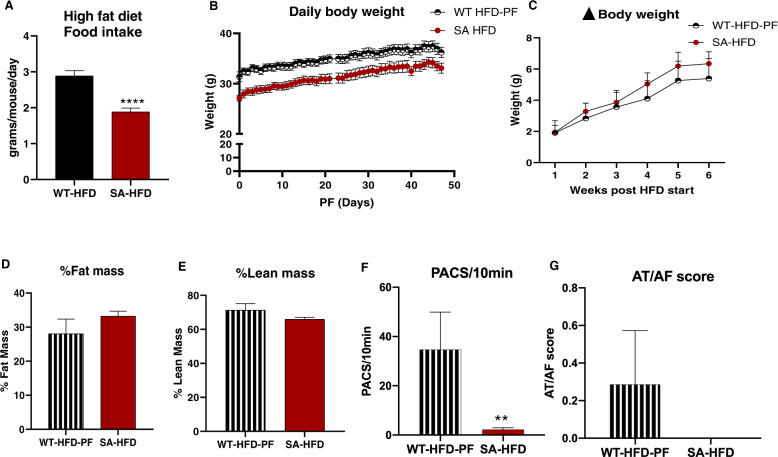
Fig. 5. Attenuating body weight gain on HFD partially mitigates susceptibility to AF in wild-type mice compared to SA knock-in mice.
A Average daily food intake of WT-HFD and SA-HFD mice on a high-fat diet. Data are presented as means ± SEM (WT-HFD n = 15, SA-HFD n = 5; ****p < 0.0001 vs WT-HFD). Wild-type mice were pair-fed (WT-HFD-PF) the same amount of HFD as SA-HFD mice for 6 weeks and B body weight C changes in body weight measured. D changes in percent fat and E lean mass measured using EchoMRI. Data are presented as means ± SEM (WT-HFD-PF n = 9, SA-HFD n = 10). F Density of pre-atrial contractions and G severity of AT/AF based on a score of 0 (none) to 4 (severe) measured following injection of epinephrine (1.5 mg/kg) and caffeine (120 mg/kg). Data are presented as means ± SEM (WT-HFD-PF n = 7, SA-HFD n = 14; **p < 0.01 vs WT-HFD-PF).