Figure 1.
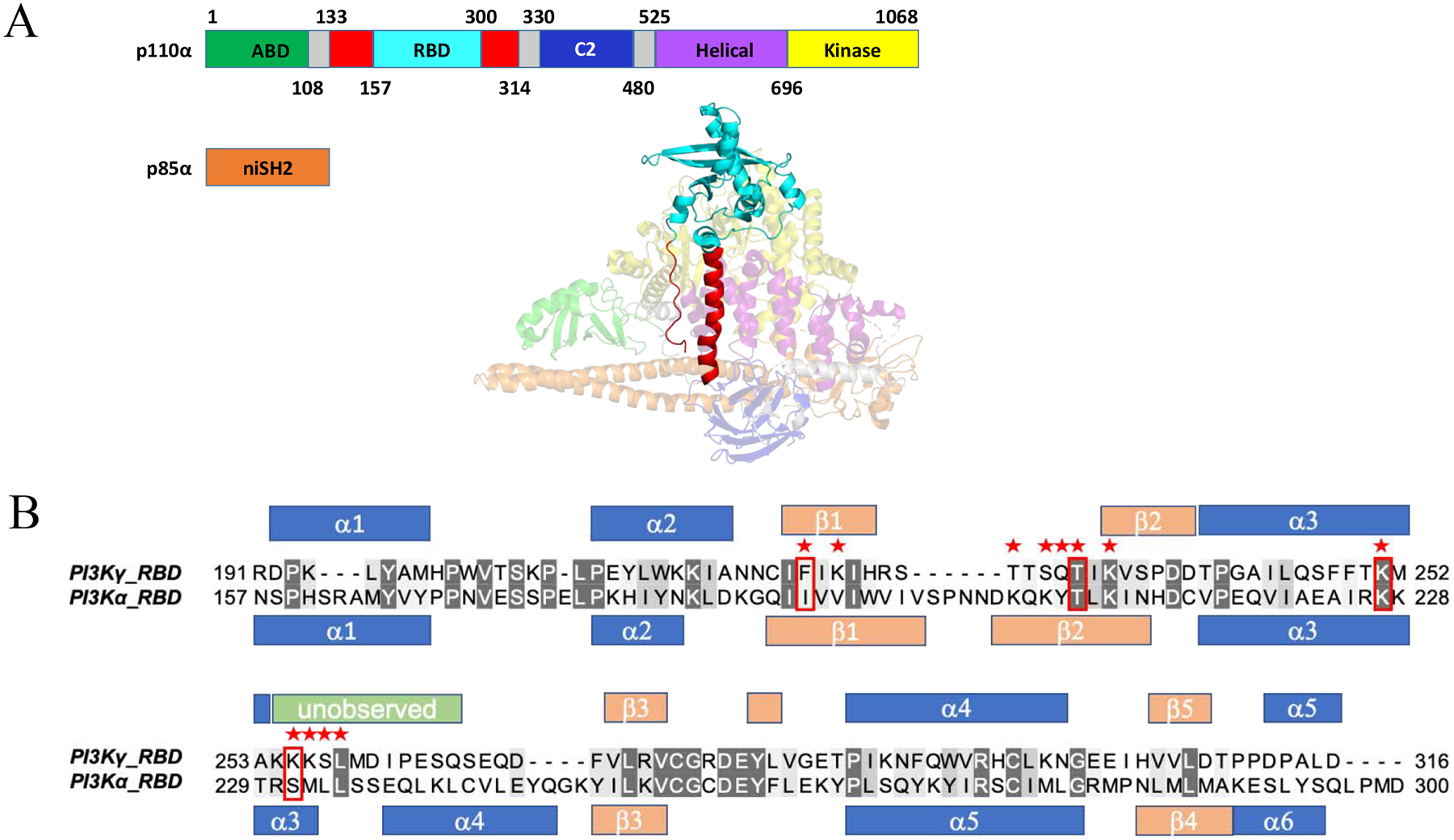
Generation of PI3Kα and PI3Kγ RAS binding domains (RBD) for high level bacterial expression. (A) Domains within the catalytic (p110α) and regulatory subunit (p85α). The adaptor binding domain (ABD) is shown in green, RBD in red (Rodriguez-Viciana et al, 1996), truncated RBD in cyan (Residues 157–300), C2 domain in blue, helical domain in purple and helical domain in yellow, with linker regions in gray. The N-terminal iSH2 domain within the regulatory subunit is shown in orange (PDB ID: 3HHM). (B) Structure-based sequence alignment for both the PI3Kγ (PDB ID: 1HE8) and truncated PI3Kα (PDB ID: 3HHM) RBDs created using PyMol {DeLano, 2002 #422}. Red stars indicate residues in PI3Kγ that contact HRASG12V in the HRASG12V/PI3Kγ crystal structure (PDB ID: 1HE8) and red boxes indicate the four residues shown to be critical for HRASG12V/PI3Kγ binding. Secondary structural elements are shown for the RBDs (α: α-helix in blue; β: β-strand in peach) of p110γ (PDB ID: 1E8X) and p110α (PDB ID: 3HHM). Unobserved residues in the p110α RBD (PDB ID: 3HHM) (Res. 254–265) are shown in green.
