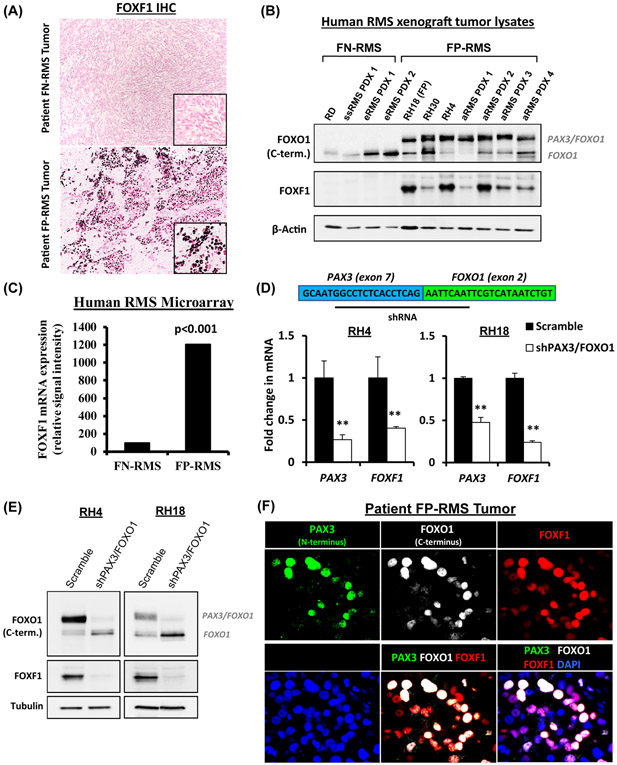
Figure 1. FOXF1 expressed in fusion-positive FP-RMS tumors.
(A) Immunostaining shows FOXF1 protein in tumors of patients with FP-RMS (n=13), but not with FN-RMS (n=11). (B) Western blots of tumor lysates show the presence of PAX3-FOXO1 and FOXF1 proteins in human RMS orthotopic xenografts. (C) Increased FOXF1 mRNA in fusion-positive FP-RMS is shown using gene expression microarrays of patient RMS tumors (ArrayExpress accession number E-MEXP-121). Groups are based on histology and fusion status. (D) Depletion of PAX3-FOXO1 decreases FOXF1 gene expression. Inhibition of PAX3-FOXO1 was performed using shRNA targeting the PAX3 and FOXO1 junction. qRT-PCR was performed, and values were normalized to β-actin (n=3). Data reported as mean ± SEM, ** p<0.01. (E) Depletion of PAX3-FOXO1 decreases FOXF1 protein levels. Western blots show efficient depletion of PAX3-FOXO1 fusion protein and FOXF1 protein. (F) FOXF1 co-localizes with PAX3-FOXO1 in FP-RMS tumors. Co-immunostaining of PAX3 (N-terminus), FOXO1 (C-terminus), and FOXF1 in a patient FP-RMS.