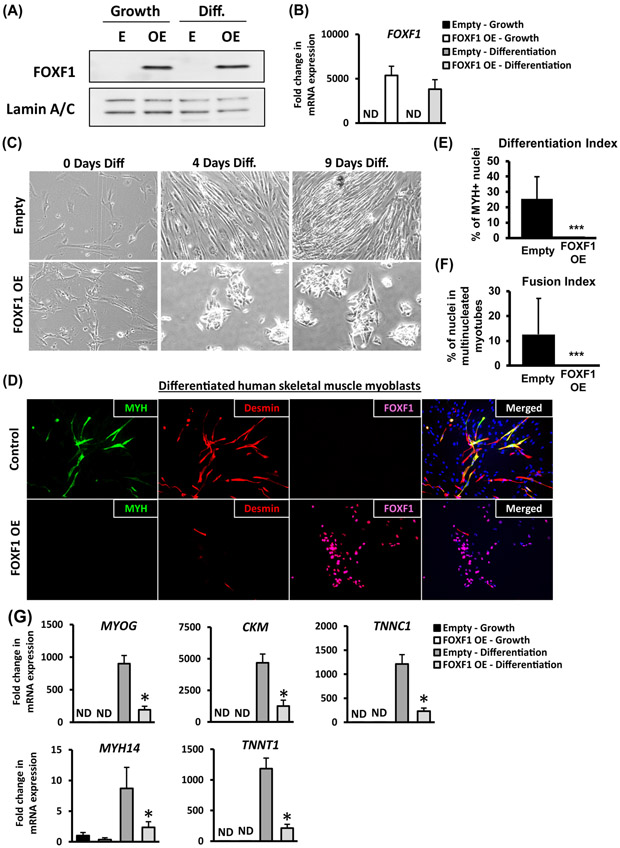
Figure 5. Ectopic expression of FOXF1 in primary human skeletal muscle myoblasts inhibits myogenic differentiation.
Primary human skeletal muscle myoblasts (HSMM) were transduced with empty (E) lentiviral plasmid or plasmid containing the human FOXF1 cDNA (OE). (A) Western blots show efficient over-expression of FOXF1 in HSMM (OE), but not in primary HSMM (E). Cell were cultured either in growth media (Growth) or in differentiation media (Diff.). Lamin A/C was used as a loading control. (B) FOXF1 mRNA in control HSMM (E) and in FOXF1 OE HSMM is shown by qRT-PCR. Values were normalized to β-actin. (C) Over-expression of FOXF1 in HSMM caused morphological changes during differentiation in vitro. (D) Immunostaining for MyH and Desmin showed a reduction in the number of MyH-positive and Desmin-positive FOXF1 OE myoblasts after 9 days in differentiation media. (E-F) Quantification of differentiation index and fusion index in control and FOXF1-expressing HSMM. A minimum of 100 nuclei were counted across three biological replicates and presented as mean ± SEM. ***p<0.001. (G) qRT-PCR shows the decrease in mRNAs of skeletal muscle differentiation markers using HSMM after 5 days in differentiation media. Values were normalized to β-actin (n=3). Data reported as mean ± SEM.