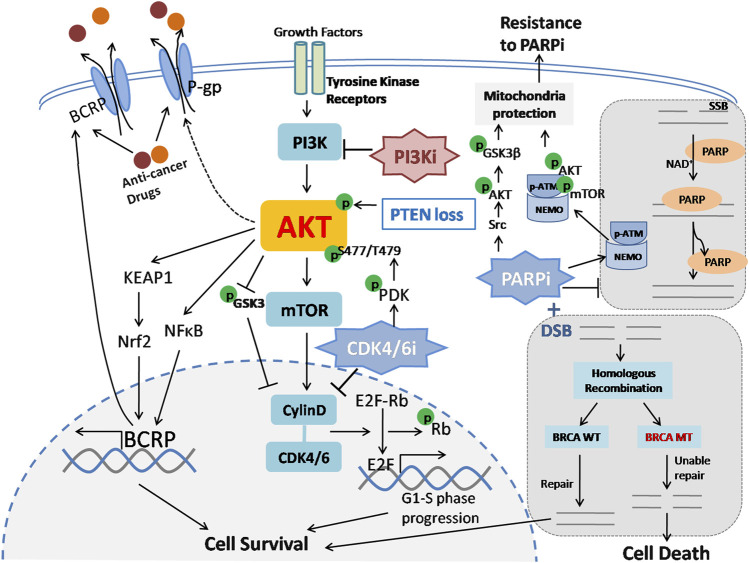
FIGURE 4.
PI3K/AKT pathway is related to chemotherapy, CDK4/6 and PARP inhibitor resistance. 1) ABC transporters, including BCRP and P-gp, enhance the efflux of chemotherapeutic drugs and cause chemoresistance. PI3K/AKT promotes BCRP transcription via the KEAP1-Nrf2 axis and NF-κB pathway and induces P-gp expression with an uncharacterized mechanism. Subsequently, drug outflow is increased through ABC transporters, which ultimately results in resistance to chemotherapy in breast cancer. ABC: ATP-binding cassette; KEAP1: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; Nrf2: nuclear factorerythroid-derived 2. 2) The CDK4/6 complex promotes Rb phosphorylation and dissociates Rb from E2F transcription factors, thus promoting cell cycle G1-S phase progression and cell survival. CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors can block this process and inhibit tumor cell proliferation. However, CDK4/CDK6 inhibition therapy leads to PI3K/AKT pathway activation via phosphorylation of AKT at the S477/T479 site by PDK1. Additionally, activated AKT can also upregulate cyclin D expression by inhibiting GSK3 phosphorylation. As a result, breast cancer cells gradually become resistant to CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors. CDK4/CDK6: Cyclin D/cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6; Rb: retinoblastoma protein. 3) PARP is activated by DNA damage and catalyzes the covalent coupling of branched chains of ADP-ribose units, thus promoting DNA repair and maintaining genomic stability. In BRCA-mutated cells, double-strand broken DNA is unable to be repaired via homologous recombination; such cells fail to repair and ultimately exhibit synthetic lethality in the presence of DNA damage and PARP inhibitors. Suppression of PARP1 activity induces AKT and its downstream target GSK3β phosphorylation via Src and facilitates cytoplasmic translocation of the pATM-NEMO complex and thereby forms a cytoprotective signalosome, both of which contribute to mitochondrial protection under oxidative stress conditions and lead to acquired resistance to PARP inhibitors. PARP: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases; SSB: Single-strand break; DSB: Double-strand break.