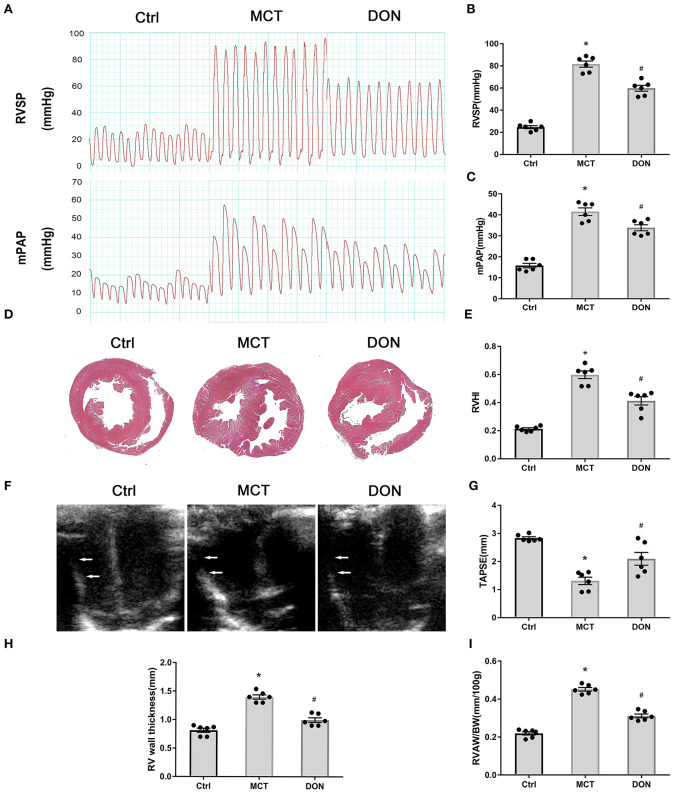
Figure 2.
DON improves hemodynamics and RV dysfunction in MCT-induced PAH rats. At the end of the study, RVSP and mPAP were measured with closed-chest technique to show the hemodynamic changes of MCT-induced rats after DON treated. The heart of rats was fixed and stained with HE to show the RV expanding and remodeling. RVHI indicates the ratio of RV weight to LV + S weight. Transthoracic echocardiography at the apical 4-chamber view to show the indicators of RV remodeling and dysfunction. (A) RVSP and mPAP measurement in experimental rats. (B) Statistical analysis of RVSP. (C) Statistical analysis of mPAP. (D) Representative HE staining of heart samples. (E) Quantitative analysis of RVHI. (F) Transthoracic echocardiography at the apical 4-chamber view. (G) Statistical analysis of TAPSE. (H) Statistical analysis of RV wall thickness. (I) Statistical analysis of the ratio of RVAW to BW. BW, body weight; Ctrl, control; DON, donepezil, HE, hematoxylin and eosin; LV, left ventricle; MCT, monocrotaline; mPAP, mean pulmonary arterial pressure; RVSP, right ventricular systolic pressure; RV, right ventricle; RVHI, RV hypertrophy index; RVAW, right ventricular anterior wall; S, septum; TAPSE, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion. *P < 0.05, vs. Ctrl group, #P < 0.05, vs. MCT group (n = 6).