Figure 1.
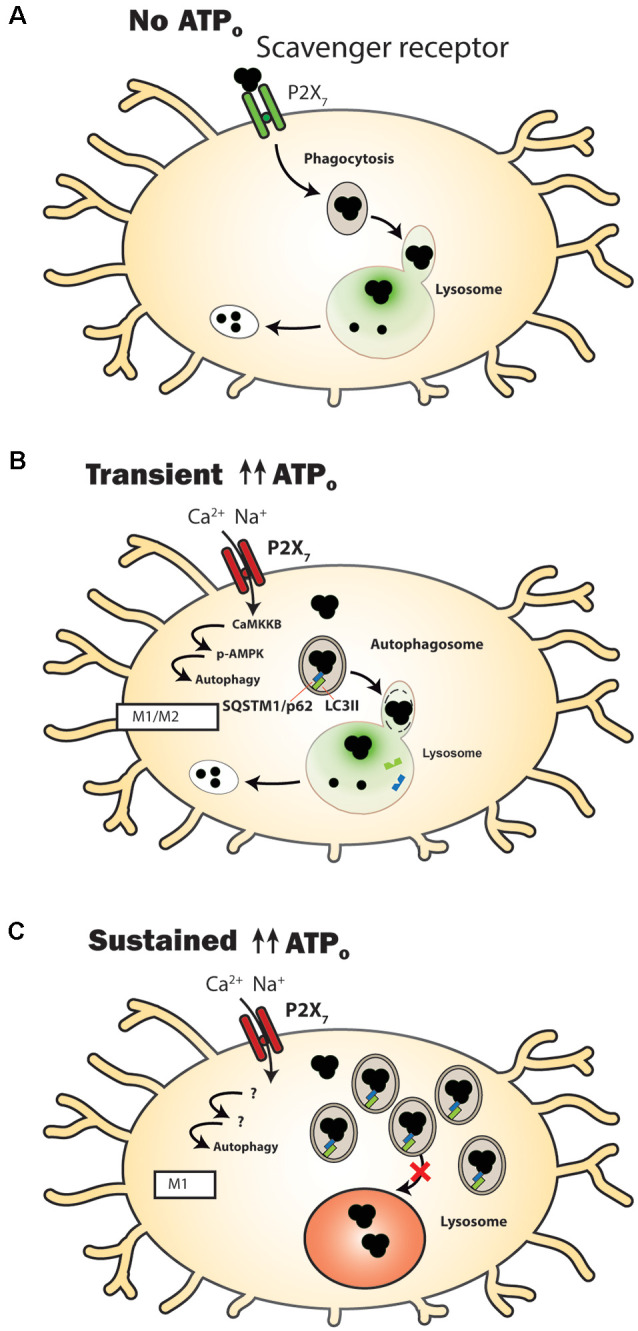
P2X7 receptor modulation of clearance pathways in microglial cells. (A) Under control conditions when extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels (ATPo) are too low to activate the P2X7 receptor, it acts as a scavenger receptor to aid in the phagocytosis of extracellular waste. The luminal pH of lysosomes in microglial cells is sufficiently acidic (green) to enable efficient degradative enzyme activity. (B) Following transient stimulation with high concentrations of ATPo, the P2X7 receptor no longer acts as a scavenger receptor. Autophagy is stimulated, shown by a transient rise in levels of autophagosomal lipid marker microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3-II (LC3-II). Material is degraded and microglia express genes and proteins associated with a mixed M1/M2 activation state. (C) A more prolonged stimulation of the P2X7 receptor leads to an elevated lysosome pH (red), with autophagosomal contents being delivered extracellularly instead of to the lysosome. Markers of accumulation, including LC3-II (green) and sequestosome-1 (SQSTM1/p62; blue) are elevated. Microglia express genes and proteins associated with an M1 activation state.
