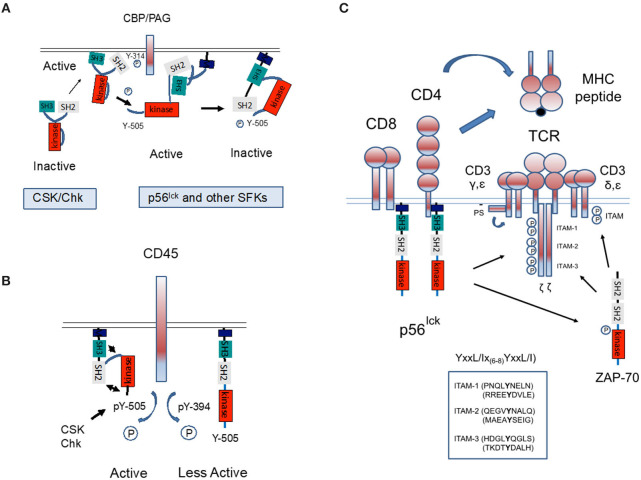
Figure 2.
Regulation of p56lck and phosphorylation of the TCR complex. (A) Regulation of p56lck kinase activity. The SH2 domain of p56lck binds to the C-terminal inhibitory Y-505, an interaction aided by SH3 domain binding to proline residues. These interactions hold the structure in a closed inactive conformation. Phosphorylation of the C-terminal Y-505 is inhibitory, while the dephosphorylation at Y-505 unfolds the kinase, unleashing its full catalytic activity accompanied by auto-phosphorylation of Y-384 within the catalytic domain. In this context, C-terminal protein kinase and related CSK-homologous kinase (Chk) bind to the anchoring protein CBP/PAG and inactivates p56lck by phosphorylation on Y-505. (B) The transmembrane protein phosphatase CD45 counterbalances the effect of CSK by preferentially dephosphorylating the inhibitory Y-505 tyrosine. However, CD45 can also dephosphorylates Y-394 to dampen kinase activity. The relative effects on Y-505 and Y-394 may be temporally regulated. (C) Model whereby CD4 and CD8-p56lck phosphorylate ITAMs on the TCRζ and CD3γ, δ, ε chains. During antigen-presentation by antigen-presenting cells (i.e., dendritic cells), coordinate binding of CD4/CD8 and the TCR to MHC antigens would bring p56lck into proximity where trans-phosphorylation would occur. p56lck also phosphorylates and activates ZAP-70.