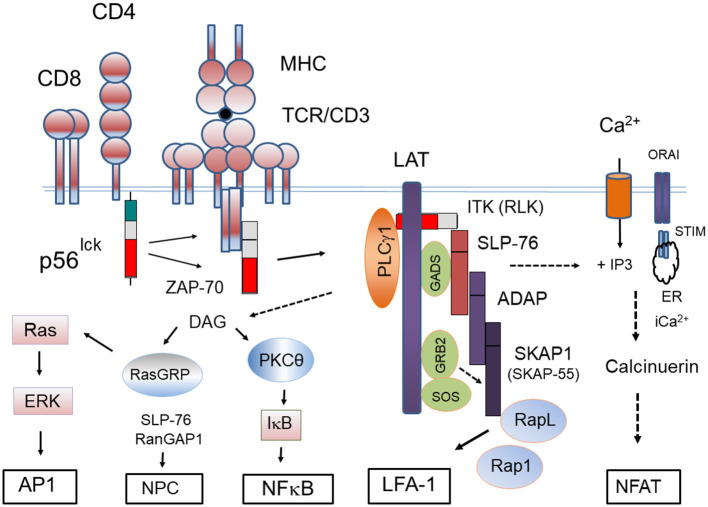
Figure 4.
Proximal signaling complexes and downstream responses initiated by the CD4/CD8-p56lck complexes. Model outlining CD4/CD8-p56lck initiation of the protein-tyrosine activation cascade. CD4/CD8-p56lck phosphorylation of TCR ITAMs leads to the recruitment and activation of ZAP-70 followed by its phosphorylation and formation of the LAT signalosome. pLAT recruits several SH2-domain-containing proteins, including phospholipase Cγ-1 (PLCγ1) growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2) and GRB2-related adaptor protein (GADS). Through its constitutive association with GADS, SLP-76 constitutively associates with LAT. Associated IL-2-inducible T-cell kinase (ITK) and resting lymphocyte kinase (RLK) phospho-activate PLCγ1 resulting in the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate to inositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 production leads to increases of intracellular free Ca2+ concentration, whereas DAG can activate both protein kinase C- (PKC-θ) and RAS guanyl nucleotide-releasing protein (RASGRP). IP3 generated from PIP2 binds to the Ca2+−permeable ion channel receptors (IP3R) in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) releasing Ca2+ from within ER stores to the cytoplasm. The ER senses intracellular Ca2+ levels through stromal interaction molecule (STIM). Depletion of intracellular Ca2+ triggers an Ca2+influx from Orai1 type plasma membrane calcium-release activated calcium (CRAC) channel. Increased intracellular Ca2+ activates a protein phosphatase, calcineurin, that dephosphorylates the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) for its nuclear translocation. pLAT also recruits the SH2 domain of GRB2 and GRB2-associated RAS guanosine nucleotide-exchange factor (GEF), son-of-sevenless (SOS) to activate p21RAS. Tyrosine-phosphorylated SLP-76 also associates with the immune cell adaptors ADAP and SKAP1. SKAP1 controls the formation of the Rap1-RapL complex needed for LFA-1 activation. SLP-76 also interacts with RanGAP1 in the nuclear complex for the increased transport of transcription factors NFAT and NFkb into the nucleus.