Table 3.
Antitubercular agents inhibition the mycobacterial respiratory system.
| No. | Target | Scaffold | SAR plan from hit | Most advanced analogue | In vivo efficacy | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | NDH-2 | Quinolinyl pyrimidines |
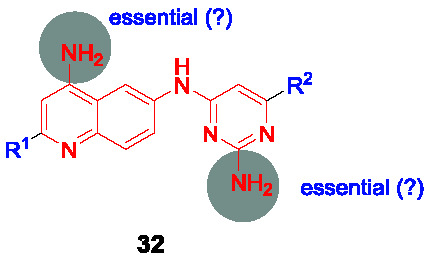
|
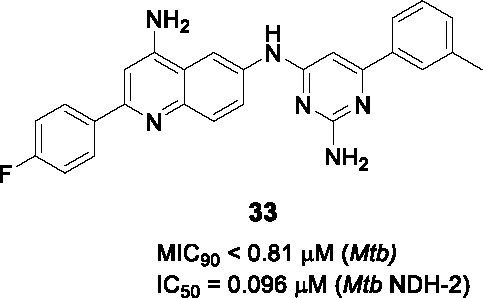
|
N/Da | (Shirude et al., 2012) |
| 1.2 | Quinolones |
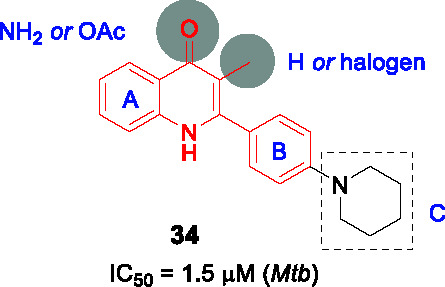
|
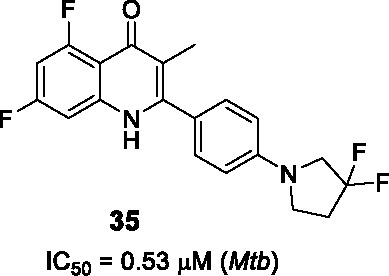
|
N/D | (Hong et al., 2017) | |
| 1.3 | 2−Mercapto quinazolinones |
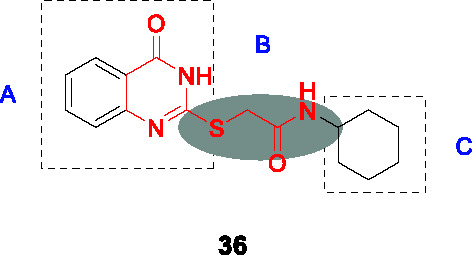
|
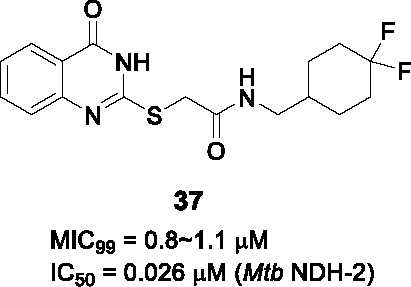
|
N/D | (Murugesan et al., 2018) | |
| 1.4 |
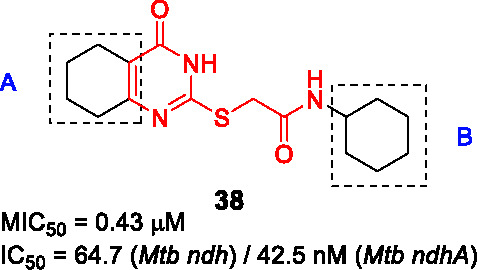
|
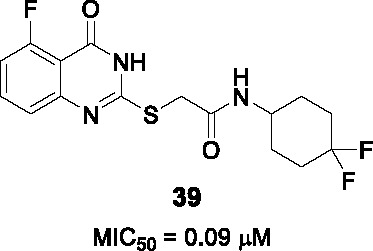
|
N/D | (Harbut et al., 2018) | ||
| 2.1 | QcrB | Alkyl benzimidazoles |
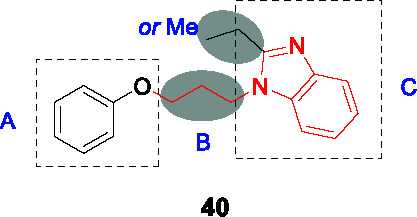
|
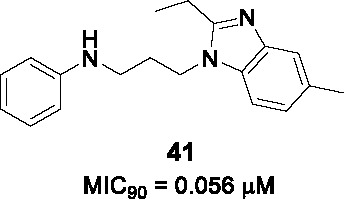
|
N/D | (Chandrasekera et al., 2015; Chandrasekera et al., 2017) |
| 2.2 | Morpholino thiophenes |
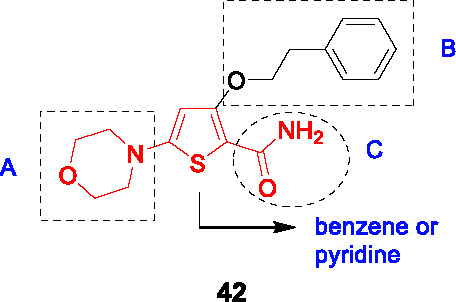
|
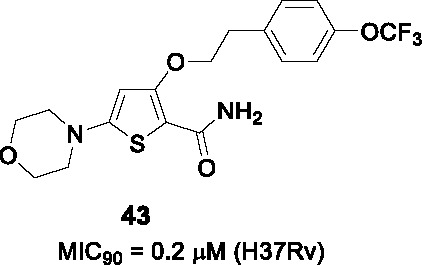
|
Yesb | (Cleghorn et al., 2018) | |
| 3.1 | MenG | Biphenyl amides |
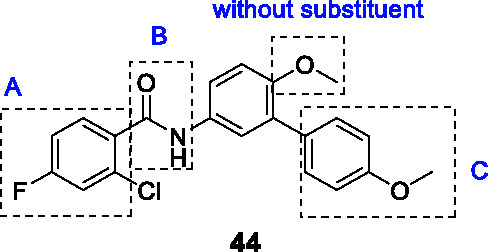
|
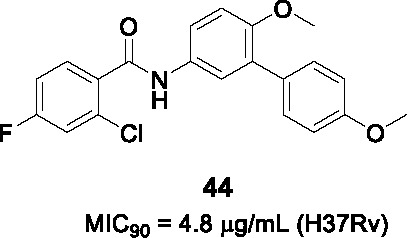
|
N/D | (Sukheja et al., 2017) |
aN/D, not determined; bYes, active in an acute TB infection mouse model.
