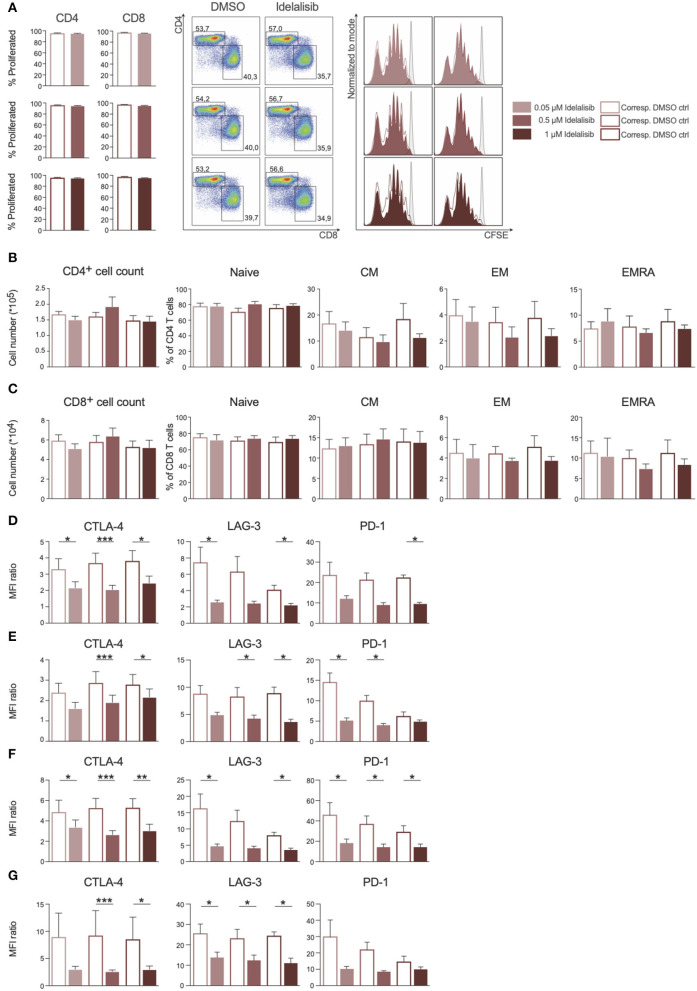
Figure 1.
Inhibition of the PI3K∂ signaling pathway by Idelalisib reduces the expression levels of inhibitory checkpoint molecules in CD3+ T cells and Treg cells. (A) Compiled data showing the percentage of proliferated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the presence of various concentrations of idelalisib or DMSO, and representative flow cytometry dot plots and histograms. (B,C) Bar charts depicting the development of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subsets: naïve, central memory (CM), effector memory (EM), and terminally differentiated effector memory cells re-expressing CD45RA (ERMA) after 6 days of coculture, with different concentrations of idelalisib or DMSO as vehicle control. (D–G) Bar graphs of MFI ratios showing the expression levels of checkpoint molecules CTLA-4, LAG-3, and PD-1 in CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, CD4+ Tregs and CD8+ Tregs after stimulation for 3 or 5 days with IL-2 and CD3/CD28 activation beads. Error bars represent mean ± SEM; *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.005, ***p ≤ 0.0005; n = 6–12 HDs.