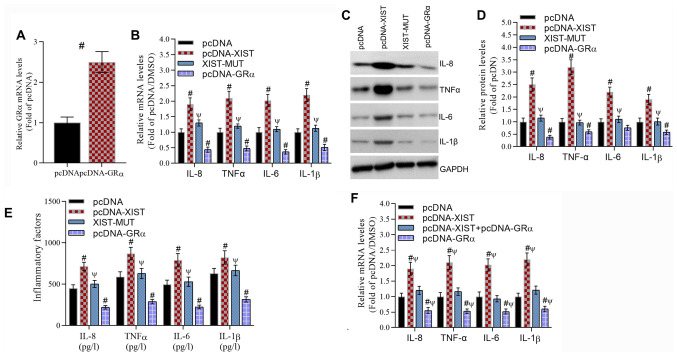
Figure 3.
XIST promotes the production of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-8, TNFα, IL-6 and IL-1β, that depend on the binding of XIST and GRα. (A) RT-qPCR data demonstrated the effect of GRα overexpression on GRα mRNA levels. #P<0.05 vs. the pcDNA group. (B) RT-qPCR data revealed the effect of XIST-WT, XIST-MUT and GRα overexpression on the mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines. #P<0.05 vs. the pcDNA group and ΨP<0.05 vs. the XIST group. (C) Representative western blotting images and (D) analyzed data demonstrated the effect of XIST-WT, XIST-MUT and GRα overexpression on the protein levels of inflammatory cytokines. #P<0.05 vs. the pcDNA group and ΨP<0.05 vs. the XIST group. (E) Analyzed data revealed the effect of XIST-WT, XIST-MUT and GRα overexpression on the protein levels of inflammatory cytokines as determined by ELISA. #P<0.05 vs. the pcDNA group and ΨP<0.05 vs. the XIST group. (F) Analyzed data demonstrated that the inhibitory effect of GRα overexpression reversed the stimulatory effect of XIST on the protein levels of inflammatory cytokines as determined by ELISA. #P<0.05 vs. the pcDNA group and ΨP<0.05 vs. the XIST+GRα group. For IL-8, IL-6 and IL-1β, n=5/group. For TNFα, n=6/group. XIST, X inactivate-specific transcript; GRα, glucocorticoid receptor α; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; WT, wild-type; MUT, mutant; IL, interleukin; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α.