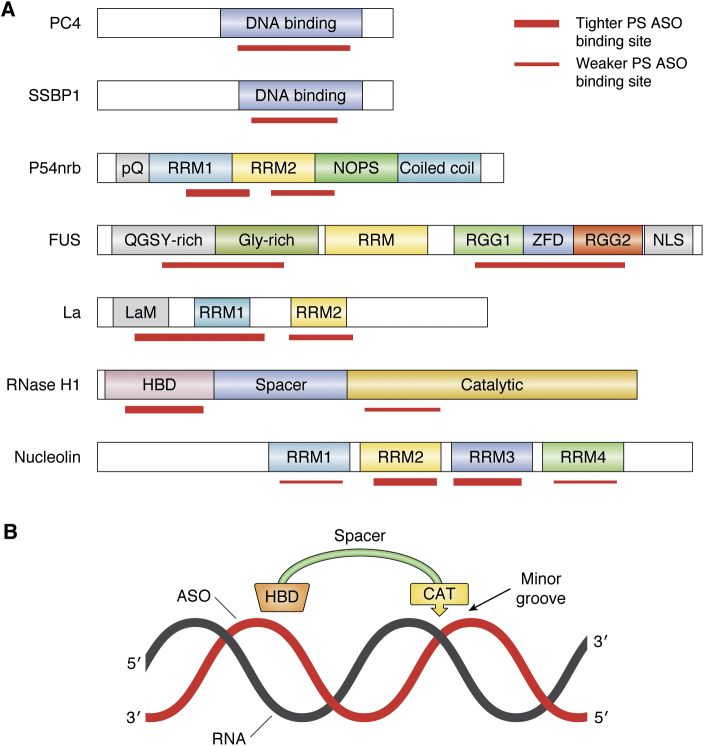
Figure 3.
Schematic prediction of the domains of model PS-ASO binding proteins.A, protein domains involved in PS-ASO binding. PS-ASO binding domains are induced with red bars. Tighter binding is marked with thicker bars. LaM, La motif; NLS, nuclear localization signal; NOPS, Nona/Paraspeckle domain; pQ, proline and glutamine-rich domain; RGG, arginine/glycine–glycine-rich domain; RRM, RNA recognition motif; ZFD, zinc-finger domain. B, schematic illustration of the relationship of HBD and catalytic domains on a heteroduplex. The HBD and Cat domains act as a caliper to measure approximately one helical turn. This enables the enzyme to bind to any duplex, but discriminate RNA/DNA heteroduplex from RNA/RNA and DNA/DNA duplexes based on slight differences in helical geometry. The catalytic domain measures the width of the minor groove and detects the presence or absence of a 2’OH and phosphate positioned properly. The enzyme is minimally processive, cleaving at most one or two nucleotides 3’ to its initial cleavage site. CAT, catalytic domain; HBD, hybrid binding domain.