Figure 1.
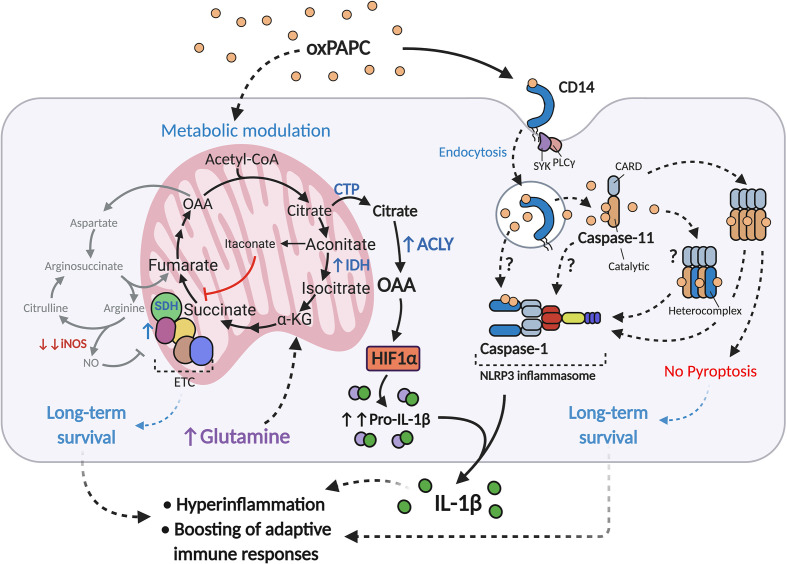
oxPAPC boosts inflammatory responses in LPS-activated macrophages. Upon LPS encounter and/or during atherosclerosis development, oxPAPC induces a metabolic remodeling state in phagocytes, termed hypermetabolism, that is characterized by 1) boosting of mitochondrial activity via iNOS inhibition and ETC protection; 2) sustaining the TCA cycle with glutamine and upregulation of IDH; and 3) upregulating ACLY. These events result in the conversion of citrate to OAA, which in turn stabilizes HIF-1α and increases production of pro-IL-1β. OxPAPC is also transported into the cytosol via the endocytic module CD14-SYK-PLCγ, where it interacts with caspse-11/4 and induces oligomerization of this enzyme. oxPAPC may also interact with caspase-1, to form caspase-11/4/5-1 hetero-complexes, or to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. These processes, termed hyperactivation, lead to IL-1β cleavage and release, but not to pyroptosis.