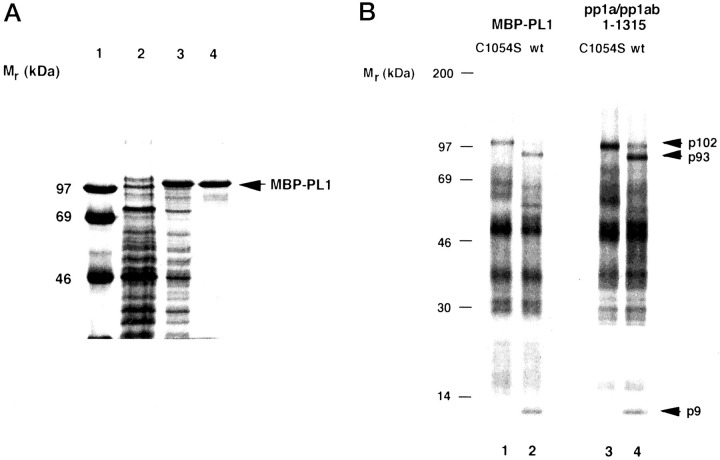
Figure 2.
Expression and purification of proteolytically activeHCoVPL1pro fused with the E. colimaltose-binding protein.A, purification of the fusion protein. MBP-PL1 was purified by affinity chromatography on amylose column from lysates of E. coli transformed with TB1[pMal-PL1] as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Aliquots taken from different stages of the purification were analyzed by 12.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, noninduced bacterial lysate; lane 3, isopropyl-1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside-induced bacterial lysate; lane 4, protein after amylose affinity chromatography. The position of MBP-PL1 is indicated. B, proteolytic activity of MBP-PL1. The trans-cleavage assay usingin vitro generated [35S]Met-labeled substrate was used to monitor proteolytic activity of purified MBP-PL1 (lanes 1 and 2) and in vitro generated, nonlabeled polypeptide containing PL1pro (pp1a/pp1ab-(1–1315)) and its mutated derivative (lanes 3 and 4). After immunoprecipitation of the cleavage reaction with IS 1720, proteins were separated by 10–17.5% gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and labeled polypeptides were visualized by autoradiography. The positions of molecular mass markers, the substrate (p102), and cleavage products (p93 and p9) are indicated. The source of enzyme was as follows: MBP-PL1 C1054S (lane 1), MBP-PL1 (lane 2), in vitro produced PL1pro C1054S (lane 3), in vitro produced PL1pro (lane 4).