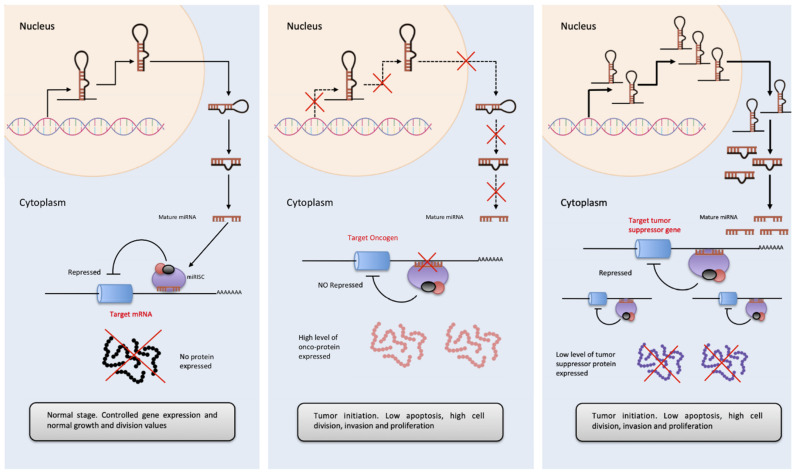
Figure 3.
OncomiRs involvement in tumor initiation process. Left. The diagram represents basal expression of miRNAs. These are released to the cytoplasm in a highly controlled amount, to exert their function by binding to the 3′-UTR of their target mRNA, inhibiting the formation of protein. Center. In the case of cancer, the expression of multiple genes is altered, if this variation causes an inhibition of OncomiRs (miRNAs that regulate oncogene expressions), these are not able to inhibit the amount of oncogenic protein, favoring proliferation, cell cycle progression as well as a decrease in apoptosis and in the tumor initiation. Right. On the contrary, in cancer, the overexpression of miRNAs acting as tumor suppressor regulators has also been observed (essentially, they are miRNAs that inhibit the expression of tumor suppressor genes). A considerable increase in the cytoplasm of OncomiRs, causes the almost disappearance of tumor suppressor proteins, favoring the development of cancer, its progression and tumor invasion.