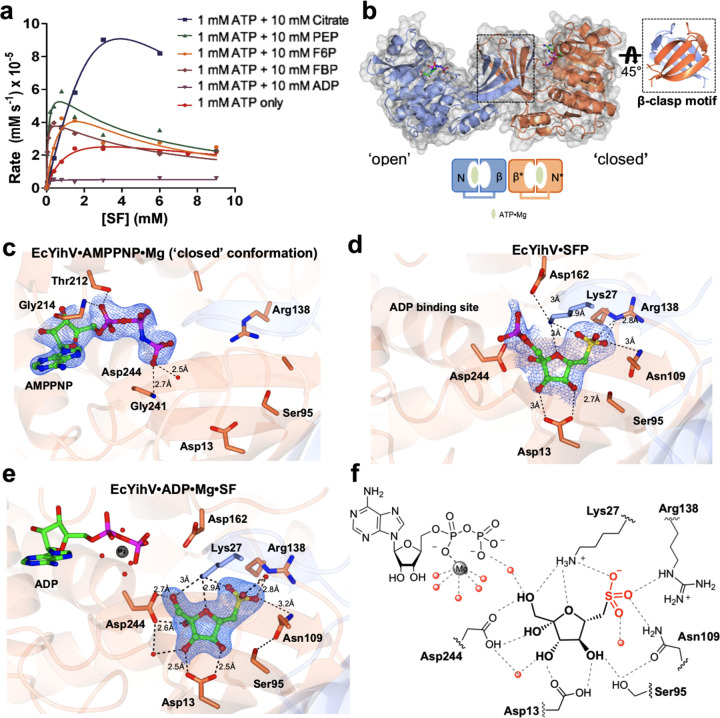
Figure 4.
Crystal structures of EcYihV SF kinase. (a) Kinetic plots showing effect of metabolites on EcYihV-catalyzed phosphorylation of SF to SFP at [ATP] = 1.0 mM. (b) (Left) EcYihV dimer in complex with AMPPNP·Mg in open and closed conformations is shown in ribbon with the two subunits shown in coral and blue. Each subunit is composed of two-domain architecture with α/β nucleotide binding domain and β-sheet “lid” domain. (Right) Lid domains of the dimer form a β-clasp dimerization motif that serves both structural and catalytic roles. (c) Close-up view of EcYihV·AMPPNP·Mg showing nucleotide binding site in the closed conformation. (d) EcYihV·SFP complex structure and active site interactions with bound SFP product molecule. (e) Close-up view of EcYihV·ADP·Mg·SF active site showing hydrogen bonding interactions in a quaternary complex. Backbone and carbon atoms of subunits A and B are shown in coral and blue, respectively, and ADP, AMPPNP, SF, and SFP are shown in cylinder format. Electron density corresponds to the 2Fo – Fc and in blue at levels of 1σ for c–e. (f) Cartoon of ligand binding pocket of EcYihV·ADP·Mg·SF complex depicting hydrogen bonding interactions with active site residues.