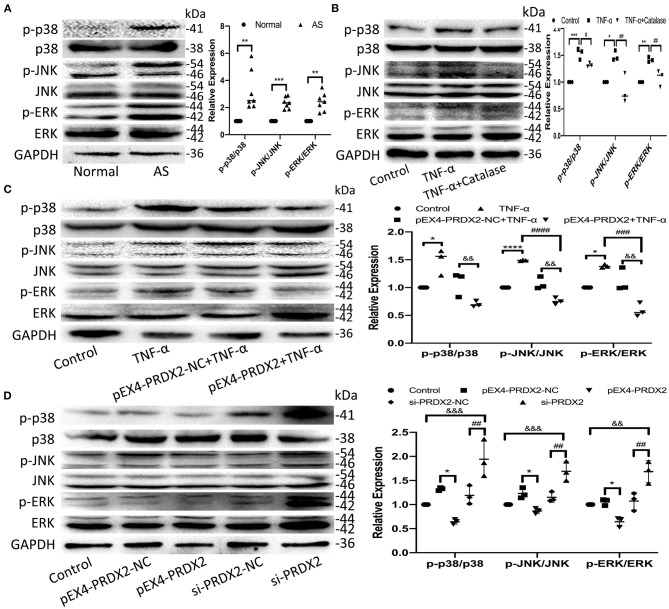
Figure 5.
PRDX2 inhibits the development of AS via the MAPK signaling pathway. (A) The expression of p-p38, p-ERK, and p-JNK was determined by Western blot in human carotid artery specimens (n = 7 humans per group, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs. normal group). (B) The expression of p-p38, p-JNK, and p-ERK was determined by Western blot in the CAVSMCs treated TNF-α and catalase (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 vs. control group, #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 vs. TNF-α group). (C) Western blot analyses for p-p38, p-ERK, and p-JNK in pEX4-PRDX2-CAVSMCs treated with TNF-α (*p < 0.05 and ****p < 0.0001 vs. control group, ###p < 0.001 and ####p < 0.0001 vs. TNF-α group, &&p < 0.01 vs. pEX4-PRDX2-NC+TNF-α group). (D) Western blot analyses for p-p38, p-JNK, and p-ERK expression in the CAVSMCs treated with pEX4-PRDX2 and si-PRDX2 transfection (*p < 0.05 vs. pEX4-PRDX2-NC group, ##p < 0.01 vs. si-PRDX2-NC group, &&p < 0.01 and &&&p < 0.001 vs. control group). The data were obtained from three independent experiments.