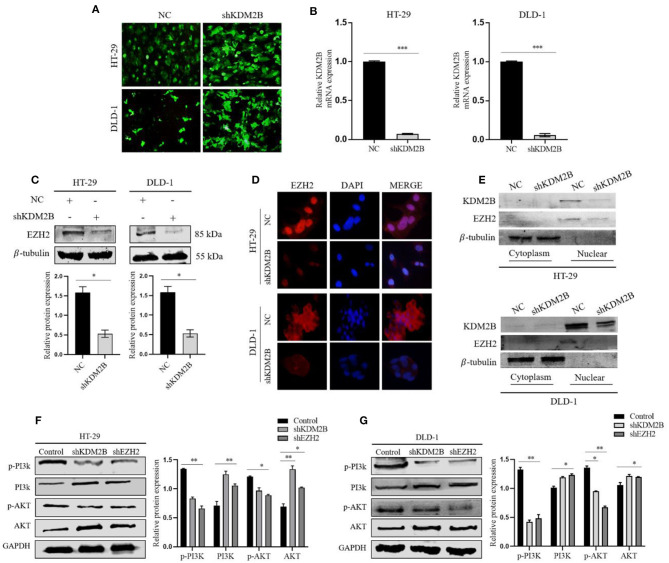
Figure 4.
KDM2B suppresses the expression of EZH2 in CRC and activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. (A) HT-29 and DLD-1 cells were infected with shRNA against KDM2B (shKDM2B) and negative control (NC), and more than 90% of cells had green fluorescence under the fluorescence microscope. Representative microscopic pictures were taken. (B) The relative expression of KDM2B mRNA was examined by real-time qRT-PCR after normalizing to GAPDH (n = 3), ***p < 0.001. The expression of EZH2 protein was determined by Western blotting and immunofluorescence after transfecting KDM2B as described in (A,C,D). (C) Shows Western blot result and representative quantification of EZH2 expression in HT-29 and DLD-1. β-tubulin was used as a loading control. (D) Immunofluorescence was performed using FITC-labeled phalloidin. The cells were stained with anti-KDM2B and anti-EZH2 antibodies (red) and DAPI (blue) and observed under a fluorescence microscope (Scale bar: 20 μm, magnification, 40 ×). (E) The cytosolic and nuclear proteins were extracted from HT-29 and DLD-1 transfected cells with shKDM2B or control vectors (NC) and the protein levels of KDM2B and EZH2 were measured using Western blot analysis. β-tubulin was used as an internal control. (F,G) The downregulation of KDM2B and EZH2 activated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. The expression levels of PI3K/AKT pathway target genes, including p-PI3K, PI3K, p-AKT, and AKT, were analyzed by Western blot Assay. GAPDH was used as a loading control. The data was statistically significant at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 as compared to negative control. The data correspond to the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.