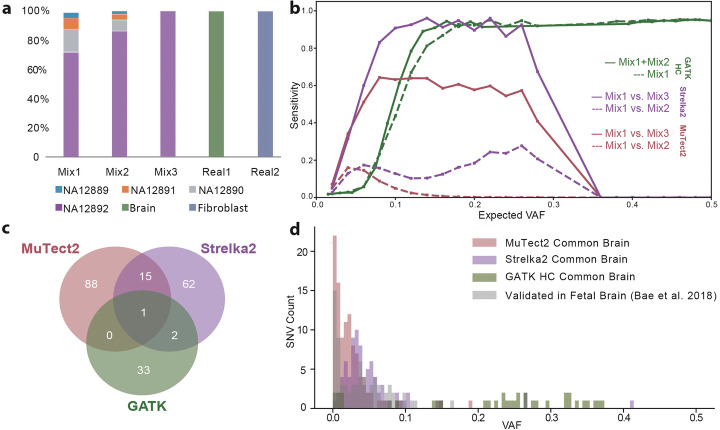
Fig. 1.
Assessment of existing tools to detect simulated mosaic SNVs in DNA mixing experiments (a, b) or candidate somatic SNVs in the common reference brain sample (c, d). a Genomic DNAs from four commonly used human lymphoblastoid cell lines were mixed at various proportions (x-axis) and subjected to WGS; germline SNPs from the cell lines are present at a range of allele frequencies (y-axis) in the different mixes and act as a proxy for mosaic SNVs. b VAF of simulated SNVs (x-axis) vs. sensitivity of detection (y-axis) for the three described SNV callers. c A Venn diagram demonstrating that existing tools are widely discordant in their ability to call mosaic SNVs present in the common brain sample. d The distribution of candidate SNV VAFs (x-axis) and the numbers of candidate mosaic SNV calls (y-axis) detected by existing tools