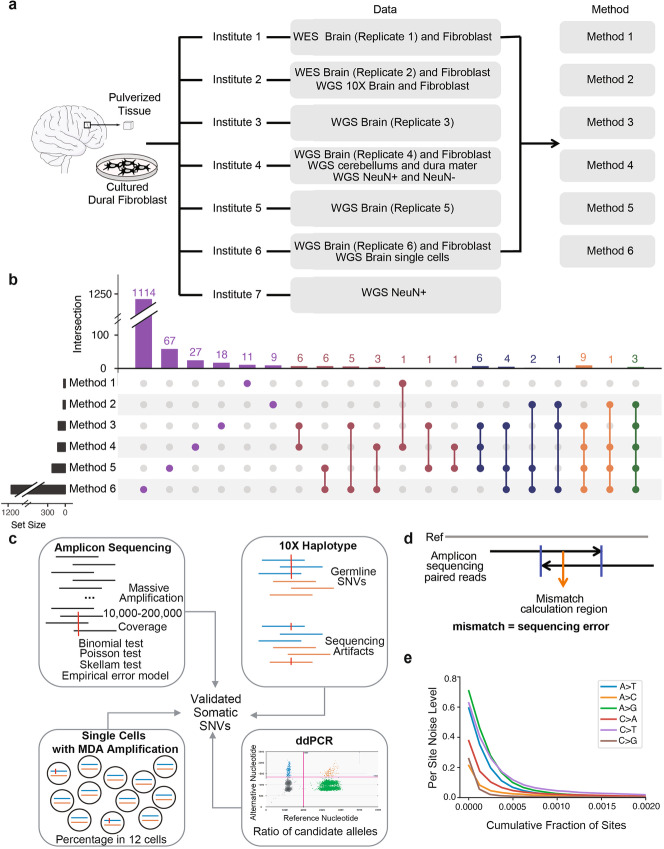
Fig. 2.
Overview of the mosaic SNV discovery and validation pipeline. a WGS or WES datasets were generated by six BSMN working groups using a commonly shared, homogenized DLPFC sample from a neurotypical individual and isogenic dural fibroblasts. Six different analytical methods initially were used to call mosaic SNVs. WGS data also was generated from sorted NeuN+ and NeuN− cells from DLPFC, cerebellum, and dura mater samples. Chromium 10X linked read sequencing data was generated from DLPFC and dural fibroblast samples. Single-cell WGS sequencing was conducted on twelve NeuN+ neurons from the DLPFC. These datasets were used to validate mosaic SNVs. b Overlap of putative mosaic SNV calls using different analytical approaches. Indicated are the numbers of mosaic SNV calls (x-axis) and the numbers of mosaic SNV calls identified using different analytical approaches (y-axis; circles with connecting lines indicate candidate SNVs identified by multiple approaches). c Candidate SNVs were subject to validation experiments using four complementary approaches. d Rationale of the empirical substitution error model applied to validate mosaic SNVs in PCR amplicon-based sequencing experiments. e An example of the empirical nucleotide error profiles encountered in a PCR amplicon-based sequencing experiment. Shown is the cumulative fraction of sites (x-axis) and per site noise levels (y-axis)